LeetCode-in-Java
3650. Minimum Cost Path with Edge Reversals
Medium
You are given a directed, weighted graph with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, and an array edges where edges[i] = [ui, vi, wi] represents a directed edge from node ui to node vi with cost wi.
Each node ui has a switch that can be used at most once: when you arrive at ui and have not yet used its switch, you may activate it on one of its incoming edges vi → ui reverse that edge to ui → vi and immediately traverse it.
The reversal is only valid for that single move, and using a reversed edge costs 2 * wi.
Return the minimum total cost to travel from node 0 to node n - 1. If it is not possible, return -1.
Example 1:
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1,3],[3,1,1],[2,3,4],[0,2,2]]
Output: 5
Explanation:
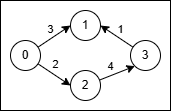
- Use the path
0 → 1(cost 3). - At node 1 reverse the original edge
3 → 1into1 → 3and traverse it at cost2 * 1 = 2. - Total cost is
3 + 2 = 5.
Example 2:
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,2,1],[2,1,1],[1,3,1],[2,3,3]]
Output: 3
Explanation:
- No reversal is needed. Take the path
0 → 2(cost 1), then2 → 1(cost 1), then1 → 3(cost 1). - Total cost is
1 + 1 + 1 = 3.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 5 * 1041 <= edges.length <= 105edges[i] = [ui, vi, wi]0 <= ui, vi <= n - 11 <= wi <= 1000
Solution
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
@SuppressWarnings({"java:S1210", "java:S2234"})
public class Solution {
private static final int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE / 2 - 1;
private int cnt;
private int[] head;
private int[] next;
private int[] to;
private int[] weight;
private static class Dist implements Comparable<Dist> {
int u;
int d;
public Dist(int u, int d) {
this.u = u;
this.d = d;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Dist o) {
return Long.compare(d, o.d);
}
}
private void init(int n, int m) {
head = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(head, -1);
next = new int[m];
to = new int[m];
weight = new int[m];
}
private void add(int u, int v, int w) {
to[cnt] = v;
weight[cnt] = w;
next[cnt] = head[u];
head[u] = cnt++;
}
private int dist(int s, int t, int n) {
PriorityQueue<Dist> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
int[] dist = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
dist[s] = 0;
queue.add(new Dist(s, dist[s]));
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Dist d = queue.remove();
int u = d.u;
if (dist[u] < d.d) {
continue;
}
if (u == t) {
return dist[t];
}
for (int i = head[u]; i != -1; i = next[i]) {
int v = to[i];
int w = weight[i];
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + w) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + w;
queue.add(new Dist(v, dist[v]));
}
}
}
return INF;
}
public int minCost(int n, int[][] edges) {
int m = edges.length;
init(n, 2 * m);
for (int[] edge : edges) {
int u = edge[0];
int v = edge[1];
int w = edge[2];
add(u, v, w);
add(v, u, 2 * w);
}
int ans = dist(0, n - 1, n);
return ans == INF ? -1 : ans;
}
}

