LeetCode-in-Java
3620. Network Recovery Pathways
Hard
You are given a directed acyclic graph of n nodes numbered from 0 to n − 1. This is represented by a 2D array edges of length m, where edges[i] = [ui, vi, costi] indicates a one‑way communication from node ui to node vi with a recovery cost of costi.
Some nodes may be offline. You are given a boolean array online where online[i] = true means node i is online. Nodes 0 and n − 1 are always online.
A path from 0 to n − 1 is valid if:
- All intermediate nodes on the path are online.
- The total recovery cost of all edges on the path does not exceed
k.
For each valid path, define its score as the minimum edge‑cost along that path.
Return the maximum path score (i.e., the largest minimum-edge cost) among all valid paths. If no valid path exists, return -1.
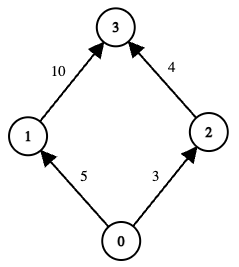
Example 1:
Input: edges = [[0,1,5],[1,3,10],[0,2,3],[2,3,4]], online = [true,true,true,true], k = 10
Output: 3
Explanation:
-
The graph has two possible routes from node 0 to node 3:
-
Path
0 → 1 → 3- Total cost =
5 + 10 = 15, which exceeds k (15 > 10), so this path is invalid.
- Total cost =
-
Path
0 → 2 → 3-
Total cost =
3 + 4 = 7 <= k, so this path is valid. -
The minimum edge‐cost along this path is
min(3, 4) = 3.
-
-
-
There are no other valid paths. Hence, the maximum among all valid path‐scores is 3.
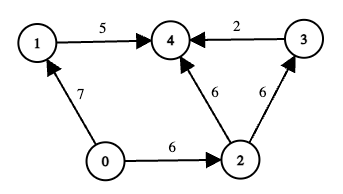
Example 2:
Input: edges = [[0,1,7],[1,4,5],[0,2,6],[2,3,6],[3,4,2],[2,4,6]], online = [true,true,true,false,true], k = 12
Output: 6
Explanation:
-
Node 3 is offline, so any path passing through 3 is invalid.
-
Consider the remaining routes from 0 to 4:
-
Path
0 → 1 → 4-
Total cost =
7 + 5 = 12 <= k, so this path is valid. -
The minimum edge‐cost along this path is
min(7, 5) = 5.
-
-
Path
0 → 2 → 3 → 4- Node 3 is offline, so this path is invalid regardless of cost.
-
Path
0 → 2 → 4-
Total cost =
6 + 6 = 12 <= k, so this path is valid. -
The minimum edge‐cost along this path is
min(6, 6) = 6.
-
-
-
Among the two valid paths, their scores are 5 and 6. Therefore, the answer is 6.
Constraints:
n == online.length2 <= n <= 5 * 1040 <= m == edges.length <=min(105, n * (n - 1) / 2)edges[i] = [ui, vi, costi]0 <= ui, vi < nui != vi0 <= costi <= 1090 <= k <= 5 * 1013online[i]is eithertrueorfalse, and bothonline[0]andonline[n − 1]aretrue.- The given graph is a directed acyclic graph.
Solution
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Solution {
private List<Integer> topologicalSort(int n, List<List<Integer>> g) {
int[] indeg = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int adjNode : g.get(i)) {
indeg[adjNode]++;
}
}
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
List<Integer> ts = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (indeg[i] == 0) {
q.offer(i);
}
}
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int u = q.poll();
ts.add(u);
for (int v : g.get(u)) {
indeg[v]--;
if (indeg[v] == 0) {
q.offer(v);
}
}
}
return ts;
}
private boolean check(
int x, int n, List<List<int[]>> adj, List<Integer> ts, boolean[] online, long k) {
long[] d = new long[n];
Arrays.fill(d, Long.MAX_VALUE);
d[0] = 0;
for (int u : ts) {
// If d[u] is reachable
if (d[u] != Long.MAX_VALUE) {
for (int[] p : adj.get(u)) {
int v = p[0];
int c = p[1];
if (c < x || !online[v]) {
continue;
}
if (d[u] + c < d[v]) {
d[v] = d[u] + c;
}
}
}
}
return d[n - 1] <= k;
}
public int findMaxPathScore(int[][] edges, boolean[] online, long k) {
int n = online.length;
// Adjacency list for graph with edge weights
List<List<int[]>> adj = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
List<List<Integer>> g = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
g.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int[] e : edges) {
int u = e[0];
int v = e[1];
int c = e[2];
adj.get(u).add(new int[] {v, c});
g.get(u).add(v);
}
List<Integer> ts = topologicalSort(n, g);
if (!check(0, n, adj, ts, online, k)) {
return -1;
}
int l = 0;
int h = 0;
for (int[] e : edges) {
h = Math.max(h, e[2]);
}
while (l < h) {
int md = l + (h - l + 1) / 2;
if (check(md, n, adj, ts, online, k)) {
l = md;
} else {
h = md - 1;
}
}
return l;
}
}

