LeetCode-in-Java
3547. Maximum Sum of Edge Values in a Graph
Hard
You are given an undirected graph of n nodes, numbered from 0 to n - 1. Each node is connected to at most 2 other nodes.
The graph consists of m edges, represented by a 2D array edges, where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi.
You have to assign a unique value from 1 to n to each node. The value of an edge will be the product of the values assigned to the two nodes it connects.
Your score is the sum of the values of all edges in the graph.
Return the maximum score you can achieve.
Example 1:

Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,0],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6]]
Output: 130
Explanation:
The diagram above illustrates an optimal assignment of values to nodes. The sum of the values of the edges is: (7 * 6) + (7 * 5) + (6 * 5) + (1 * 3) + (3 * 4) + (4 * 2) = 130.
Example 2:
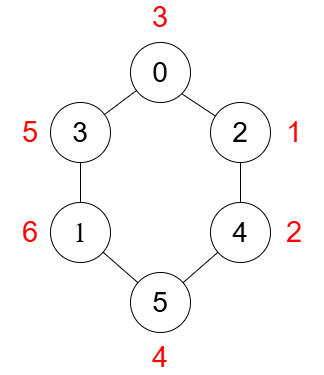
Input: n = 6, edges = [[0,3],[4,5],[2,0],[1,3],[2,4],[1,5]]
Output: 82
Explanation:
The diagram above illustrates an optimal assignment of values to nodes. The sum of the values of the edges is: (1 * 2) + (2 * 4) + (4 * 6) + (6 * 5) + (5 * 3) + (3 * 1) = 82.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 5 * 104m == edges.length1 <= m <= nedges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nai != bi- There are no repeated edges.
- Each node is connected to at most 2 other nodes.
Solution
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class Solution {
private int[] p;
private boolean[] c;
private int[] s;
public long maxScore(int n, int[][] edges) {
initializeArrays(n);
processEdges(edges);
List<Integer> circles = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> chains = new ArrayList<>();
findParentsAndUpdateCircles();
collectCirclesAndChains(circles, chains);
Collections.sort(circles);
chains.sort((a, b) -> Integer.compare(b, a));
return calculateScore(n, circles, chains);
}
private void initializeArrays(int n) {
p = new int[n];
c = new boolean[n];
s = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
p[i] = i;
s[i] = 1;
}
}
private void processEdges(int[][] edges) {
for (int[] ele : edges) {
join(ele[0], ele[1]);
}
}
private void findParentsAndUpdateCircles() {
for (int i = 0; i < p.length; i++) {
p[i] = findParent(i);
if (c[i]) {
c[p[i]] = true;
}
}
}
private void collectCirclesAndChains(List<Integer> circles, List<Integer> chains) {
for (int i = 0; i < p.length; i++) {
if (p[i] == i) {
int size = s[i];
if (c[i]) {
circles.add(size);
} else {
chains.add(size);
}
}
}
}
private long calculateScore(int n, List<Integer> circles, List<Integer> chains) {
long ret = 0;
int start = n;
ret += processCircles(circles, start);
start = n - getTotalCircleSize(circles);
ret += processChains(chains, start);
return ret;
}
private int getTotalCircleSize(List<Integer> circles) {
return circles.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).sum();
}
private long processCircles(List<Integer> circles, int start) {
long ret = 0;
for (int size : circles) {
if (size == 1) {
continue;
}
int[] temp = createTempArray(size, start);
long pro = calculateProduct(temp, true);
ret += pro;
start = start - size;
}
return ret;
}
private long processChains(List<Integer> chains, int start) {
long ret = 0;
for (int size : chains) {
if (size == 1) {
continue;
}
int[] temp = createTempArray(size, start);
long pro = calculateProduct(temp, false);
ret += pro;
start = start - size;
}
return ret;
}
private int[] createTempArray(int size, int start) {
int[] temp = new int[size];
int ptr1 = 0;
int ptr2 = size - 1;
int curStart = start - size + 1;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
temp[ptr1++] = curStart + i;
} else {
temp[ptr2--] = curStart + i;
}
}
return temp;
}
private long calculateProduct(int[] temp, boolean isCircle) {
long pro = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < temp.length; i++) {
pro += (long) temp[i] * temp[i - 1];
}
if (isCircle) {
pro += (long) temp[0] * temp[temp.length - 1];
}
return pro;
}
private int findParent(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = findParent(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
private void join(int a, int b) {
int bp = findParent(a);
int ap = findParent(b);
if (bp == ap) {
c[bp] = true;
return;
}
int s1 = s[ap];
int s2 = s[bp];
if (s1 > s2) {
p[bp] = ap;
s[ap] += s[bp];
} else {
p[ap] = bp;
s[bp] += s[ap];
}
}
}

