LeetCode-in-Java
3493. Properties Graph
Medium
You are given a 2D integer array properties having dimensions n x m and an integer k.
Define a function intersect(a, b) that returns the number of distinct integers common to both arrays a and b.
Construct an undirected graph where each index i corresponds to properties[i]. There is an edge between node i and node j if and only if intersect(properties[i], properties[j]) >= k, where i and j are in the range [0, n - 1] and i != j.
Return the number of connected components in the resulting graph.
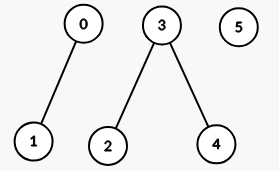
Example 1:
Input: properties = [[1,2],[1,1],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6],[7,7]], k = 1
Output: 3
Explanation:
The graph formed has 3 connected components:
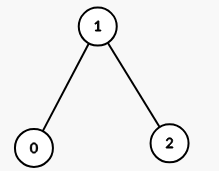
Example 2:
Input: properties = [[1,2,3],[2,3,4],[4,3,5]], k = 2
Output: 1
Explanation:
The graph formed has 1 connected component:
Example 3:
Input: properties = [[1,1],[1,1]], k = 2
Output: 2
Explanation:
intersect(properties[0], properties[1]) = 1, which is less than k. This means there is no edge between properties[0] and properties[1] in the graph.
Constraints:
1 <= n == properties.length <= 1001 <= m == properties[i].length <= 1001 <= properties[i][j] <= 1001 <= k <= m
Solution
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.BitSet;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
public class Solution {
private int[] parent;
public int numberOfComponents(int[][] properties, int k) {
List<List<Integer>> al = convertToList(properties);
int n = al.size();
List<BitSet> bs = new ArrayList<>(n);
for (List<Integer> integers : al) {
BitSet bitset = new BitSet(101);
for (int num : integers) {
bitset.set(num);
}
bs.add(bitset);
}
parent = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
BitSet temp = (BitSet) bs.get(i).clone();
temp.and(bs.get(j));
int common = temp.cardinality();
if (common >= k) {
unionn(i, j);
}
}
}
Set<Integer> comps = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
comps.add(findp(i));
}
return comps.size();
}
private int findp(int x) {
if (parent[x] != x) {
parent[x] = findp(parent[x]);
}
return parent[x];
}
private void unionn(int a, int b) {
int pa = findp(a);
int pb = findp(b);
if (pa != pb) {
parent[pa] = pb;
}
}
private List<List<Integer>> convertToList(int[][] arr) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] row : arr) {
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
for (int num : row) {
temp.add(num);
}
list.add(temp);
}
return list;
}
}

