LeetCode-in-Java
3419. Minimize the Maximum Edge Weight of Graph
Medium
You are given two integers, n and threshold, as well as a directed weighted graph of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1. The graph is represented by a 2D integer array edges, where edges[i] = [Ai, Bi, Wi] indicates that there is an edge going from node Ai to node Bi with weight Wi.
You have to remove some edges from this graph (possibly none), so that it satisfies the following conditions:
- Node 0 must be reachable from all other nodes.
- The maximum edge weight in the resulting graph is minimized.
- Each node has at most
thresholdoutgoing edges.
Return the minimum possible value of the maximum edge weight after removing the necessary edges. If it is impossible for all conditions to be satisfied, return -1.
Example 1:
Input: n = 5, edges = [[1,0,1],[2,0,2],[3,0,1],[4,3,1],[2,1,1]], threshold = 2
Output: 1
Explanation:
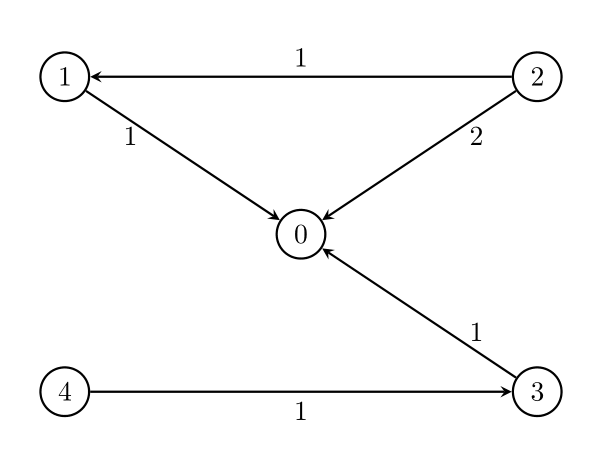
Remove the edge 2 -> 0. The maximum weight among the remaining edges is 1.
Example 2:
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1,1],[0,2,2],[0,3,1],[0,4,1],[1,2,1],[1,4,1]], threshold = 1
Output: -1
Explanation:
It is impossible to reach node 0 from node 2.
Example 3:
Input: n = 5, edges = [[1,2,1],[1,3,3],[1,4,5],[2,3,2],[3,4,2],[4,0,1]], threshold = 1
Output: 2
Explanation:
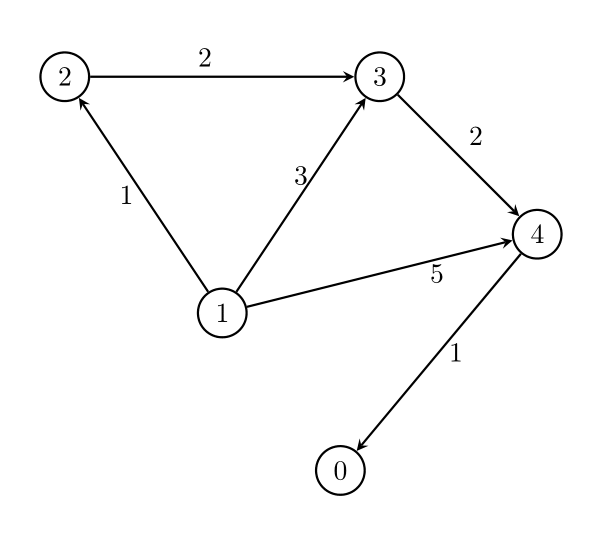
Remove the edges 1 -> 3 and 1 -> 4. The maximum weight among the remaining edges is 2.
Example 4:
Input: n = 5, edges = [[1,2,1],[1,3,3],[1,4,5],[2,3,2],[4,0,1]], threshold = 1
Output: -1
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 1051 <= threshold <= n - 11 <= edges.length <= min(105, n * (n - 1) / 2).edges[i].length == 30 <= Ai, Bi < nAi != Bi1 <= Wi <= 106- There may be multiple edges between a pair of nodes, but they must have unique weights.
Solution
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "unused", "java:S1172"})
public class Solution {
private ArrayList<ArrayList<Pair>> revadj;
private static class Pair {
int node;
int weight;
public Pair(int node, int weight) {
this.node = node;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
public int minMaxWeight(int n, int[][] edges, int threshold) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Pair>> adj = new ArrayList<>();
revadj = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= n + 1; i++) {
adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
revadj.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int[] edge : edges) {
int u = edge[0];
int v = edge[1];
int wt = edge[2];
adj.get(u).add(new Pair(v, wt));
revadj.get(v).add(new Pair(u, wt));
}
if (!check(n)) {
return -1;
}
int[] dist = new int[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(dist, (int) (1e9));
dist[0] = 0;
Queue<Pair> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(new Pair(0, 0));
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int u = q.peek().node;
int currMax = q.peek().weight;
q.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < revadj.get(u).size(); i++) {
int v = revadj.get(u).get(i).node;
int wt = revadj.get(u).get(i).weight;
if (dist[v] > Math.max(wt, currMax)) {
dist[v] = Math.max(wt, currMax);
q.offer(new Pair(v, dist[v]));
}
}
}
int maxi = dist[0];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
maxi = Math.max(maxi, dist[i]);
}
return maxi;
}
private boolean check(int n) {
int[] vis = new int[n];
ArrayList<Integer> nodes = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(0, vis, nodes);
return nodes.size() == n;
}
private void dfs(int u, int[] vis, ArrayList<Integer> nodes) {
nodes.add(u);
vis[u] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < revadj.get(u).size(); i++) {
int v = revadj.get(u).get(i).node;
if (vis[v] == 0) {
dfs(v, vis, nodes);
}
}
}
}

