LeetCode-in-Java
3378. Count Connected Components in LCM Graph
Hard
You are given an array of integers nums of size n and a positive integer threshold.
There is a graph consisting of n nodes with the ith node having a value of nums[i]. Two nodes i and j in the graph are connected via an undirected edge if lcm(nums[i], nums[j]) <= threshold.
Return the number of connected components in this graph.
A connected component is a subgraph of a graph in which there exists a path between any two vertices, and no vertex of the subgraph shares an edge with a vertex outside of the subgraph.
The term lcm(a, b) denotes the least common multiple of a and b.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,4,8,3,9], threshold = 5
Output: 4
Explanation:
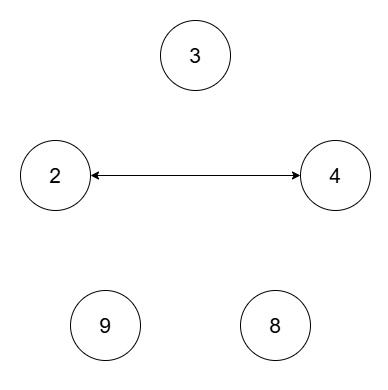
The four connected components are (2, 4), (3), (8), (9).
Example 2:
Input: nums = [2,4,8,3,9,12], threshold = 10
Output: 2
Explanation:
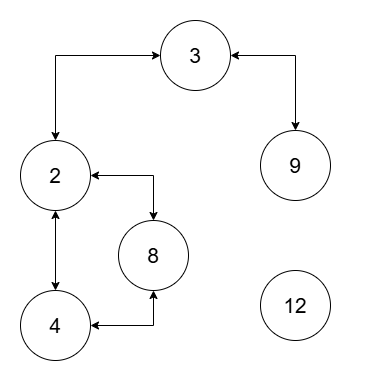
The two connected components are (2, 3, 4, 8, 9), and (12).
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1051 <= nums[i] <= 109- All elements of
numsare unique. 1 <= threshold <= 2 * 105
Solution
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class Solution {
private static class Unionfind {
int[] parent;
int[] rank;
int totalComponents;
public Unionfind(int n) {
parent = new int[n];
rank = new int[n];
totalComponents = n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
public int find(int u) {
if (parent[u] == u) {
return u;
}
parent[u] = find(parent[u]);
return parent[u];
}
public void union(int u, int v) {
int parentU = find(u);
int parentV = find(v);
if (parentU != parentV) {
totalComponents--;
if (rank[parentU] == rank[parentV]) {
parent[parentV] = parentU;
rank[parentU]++;
} else if (rank[parentU] > rank[parentV]) {
parent[parentV] = parentU;
} else {
parent[parentU] = parentV;
}
}
}
}
public int countComponents(int[] nums, int threshold) {
List<Integer> goodNums = new ArrayList<>();
int totalNums = nums.length;
for (int num : nums) {
if (num <= threshold) {
goodNums.add(num);
}
}
if (goodNums.isEmpty()) {
return totalNums;
}
Unionfind uf = new Unionfind(goodNums.size());
int[] presentElements = new int[threshold + 1];
Arrays.fill(presentElements, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < goodNums.size(); i++) {
presentElements[goodNums.get(i)] = i;
}
for (int d : goodNums) {
for (int i = d; i <= threshold; i += d) {
if (presentElements[i] == -1) {
presentElements[i] = presentElements[d];
} else if (presentElements[i] != presentElements[d]) {
uf.union(presentElements[i], presentElements[d]);
}
}
}
return uf.totalComponents + totalNums - goodNums.size();
}
}

