LeetCode-in-Java
3311. Construct 2D Grid Matching Graph Layout
Hard
You are given a 2D integer array edges representing an undirected graph having n nodes, where edges[i] = [ui, vi] denotes an edge between nodes ui and vi.
Construct a 2D grid that satisfies these conditions:
- The grid contains all nodes from
0ton - 1in its cells, with each node appearing exactly once. - Two nodes should be in adjacent grid cells (horizontally or vertically) if and only if there is an edge between them in
edges.
It is guaranteed that edges can form a 2D grid that satisfies the conditions.
Return a 2D integer array satisfying the conditions above. If there are multiple solutions, return any of them.
Example 1:
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[2,3]]
Output: [[3,1],[2,0]]
Explanation:
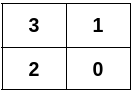
Example 2:
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[1,3],[2,3],[2,4]]
Output: [[4,2,3,1,0]]
Explanation:

Example 3:
Input: n = 9, edges = [[0,1],[0,4],[0,5],[1,7],[2,3],[2,4],[2,5],[3,6],[4,6],[4,7],[6,8],[7,8]]
Output: [[8,6,3],[7,4,2],[1,0,5]]
Explanation:
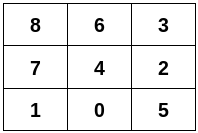
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 5 * 1041 <= edges.length <= 105edges[i] = [ui, vi]0 <= ui < vi < n- All the edges are distinct.
- The input is generated such that
edgescan form a 2D grid that satisfies the conditions.
Solution
import java.util.ArrayList;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public class Solution {
public int[][] constructGridLayout(int n, int[][] edges) {
final int[] cs = new int[n];
final ArrayList<Integer>[] als = new ArrayList[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
als[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int[] e : edges) {
cs[e[0]]++;
cs[e[1]]++;
als[e[0]].add(e[1]);
als[e[1]].add(e[0]);
}
int min = 4;
for (int a : cs) {
min = Math.min(min, a);
}
final boolean[] seen = new boolean[n];
int[][] res;
int st = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (cs[i] == min) {
st = i;
break;
}
}
if (min == 1) {
res = new int[1][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
res[0][i] = st;
seen[st] = true;
if (i + 1 < n) {
for (int a : als[st]) {
if (!seen[a]) {
st = a;
break;
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
int row2 = -1;
for (int a : als[st]) {
if (cs[a] == min) {
row2 = a;
break;
}
}
if (row2 >= 0) {
return getInts(n, st, row2, seen, als);
}
return getInts(n, seen, st, als, cs);
}
private int[][] getInts(int n, boolean[] seen, int st, ArrayList<Integer>[] als, int[] cs) {
int[][] res;
final ArrayList<Integer> al = new ArrayList<>();
boolean f = true;
seen[st] = true;
al.add(st);
while (f) {
f = false;
for (int a : als[st]) {
if (!seen[a] && cs[a] <= 3) {
seen[a] = true;
al.add(a);
if (cs[a] == 3) {
f = true;
st = a;
}
break;
}
}
}
res = new int[n / al.size()][al.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < res[0].length; ++i) {
res[0][i] = al.get(i);
}
for (int i = 1; i < res.length; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < res[0].length; ++j) {
for (int a : als[res[i - 1][j]]) {
if (!seen[a]) {
res[i][j] = a;
seen[a] = true;
break;
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
private int[][] getInts(int n, int st, int row2, boolean[] seen, ArrayList<Integer>[] als) {
int[][] res;
res = new int[2][n / 2];
res[0][0] = st;
res[1][0] = row2;
seen[st] = seen[row2] = true;
for (int i = 1; i < res[0].length; ++i) {
for (int a : als[res[0][i - 1]]) {
if (!seen[a]) {
res[0][i] = a;
seen[a] = true;
break;
}
}
for (int a : als[res[1][i - 1]]) {
if (!seen[a]) {
res[1][i] = a;
seen[a] = true;
break;
}
}
}
return res;
}
}

