LeetCode-in-Java
3249. Count the Number of Good Nodes
Medium
There is an undirected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, and rooted at node 0. You are given a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
A node is good if all the subtrees rooted at its children have the same size.
Return the number of good nodes in the given tree.
A subtree of treeName is a tree consisting of a node in treeName and all of its descendants.
Example 1:
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,5],[2,6]]
Output: 7
Explanation:
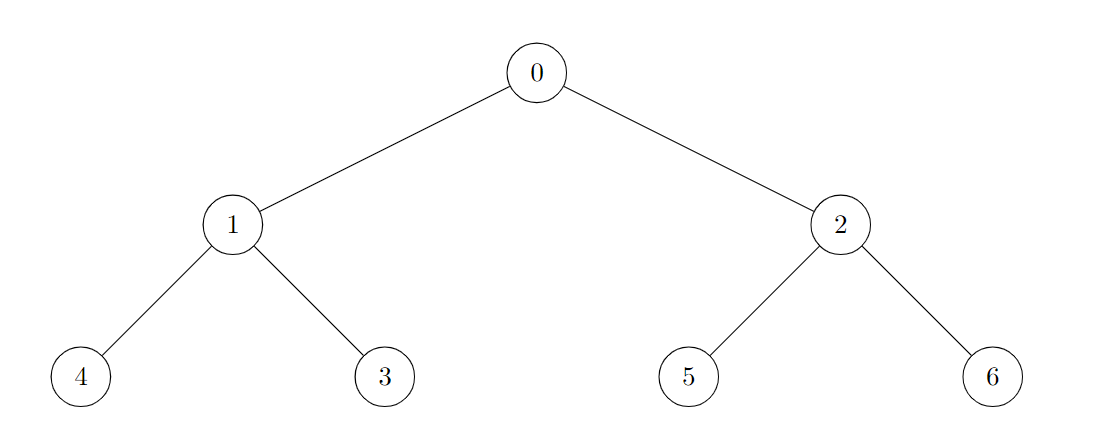
All of the nodes of the given tree are good.
Example 2:
Input: edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[0,5],[1,6],[2,7],[3,8]]
Output: 6
Explanation:
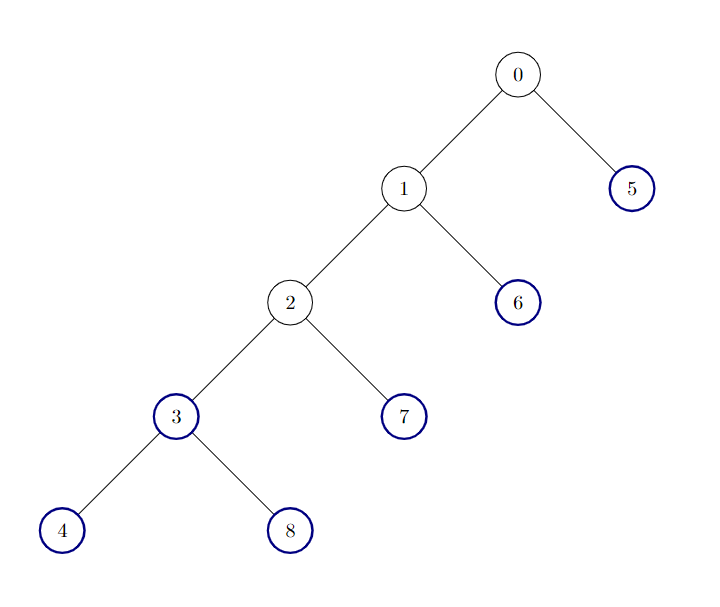
There are 6 good nodes in the given tree. They are colored in the image above.
Example 3:
Input: edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[1,3],[1,4],[0,5],[5,6],[6,7],[7,8],[0,9],[9,10],[9,12],[10,11]]
Output: 12
Explanation:
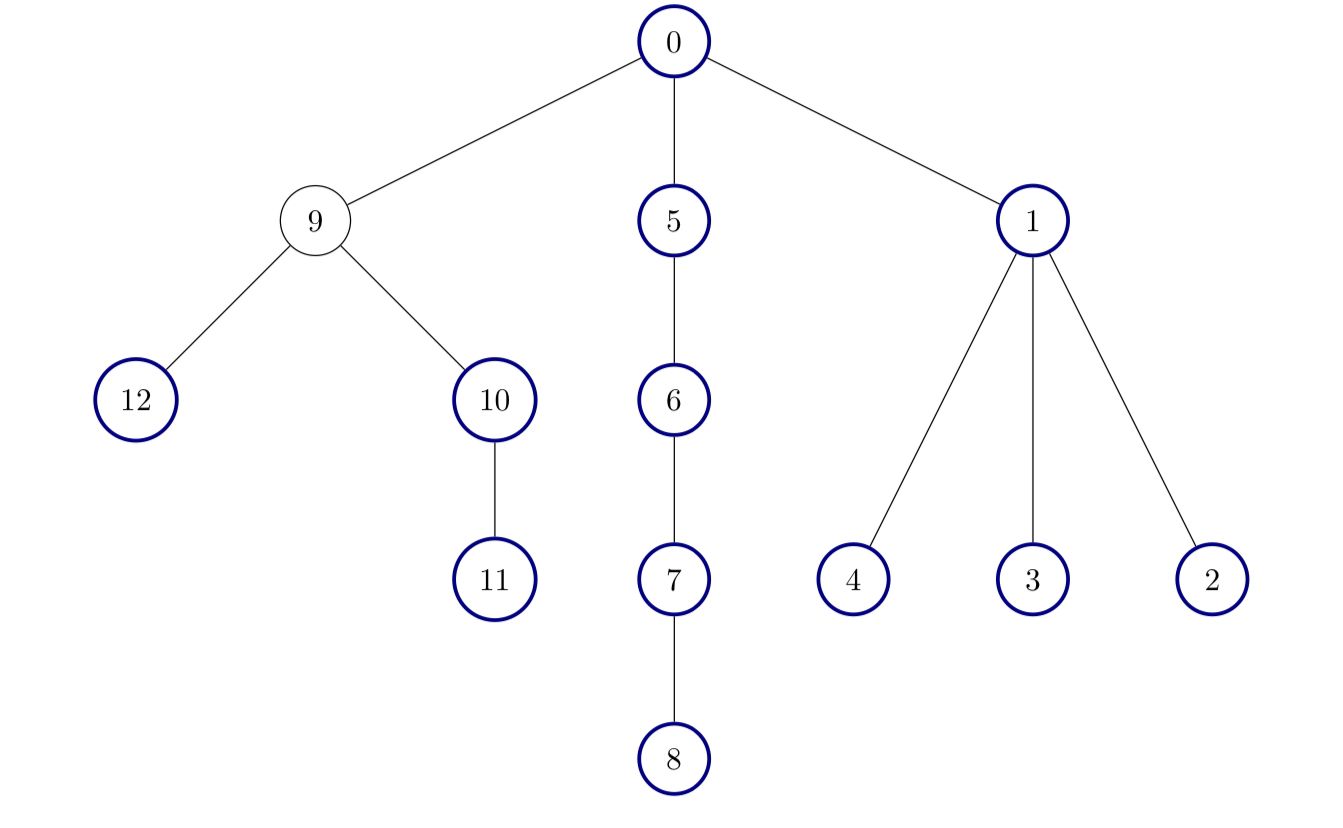
All nodes except node 9 are good.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 105edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < n- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree.
Solution
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Solution {
private int count = 0;
public int countGoodNodes(int[][] edges) {
int n = edges.length + 1;
TNode[] nodes = new TNode[n];
nodes[0] = new TNode(0);
for (int[] edge : edges) {
int a = edge[0];
int b = edge[1];
if (nodes[b] != null && nodes[a] == null) {
nodes[a] = new TNode(a);
nodes[b].children.add(nodes[a]);
} else {
if (nodes[a] == null) {
nodes[a] = new TNode(a);
}
if (nodes[b] == null) {
nodes[b] = new TNode(b);
}
nodes[a].children.add(nodes[b]);
}
}
sizeOfTree(nodes[0]);
return count;
}
private int sizeOfTree(TNode node) {
if (node.size > 0) {
return node.size;
}
List<TNode> children = node.children;
if (children.isEmpty()) {
count++;
node.size = 1;
return 1;
}
int size = sizeOfTree(children.get(0));
int sum = size;
boolean goodNode = true;
for (int i = 1; i < children.size(); ++i) {
TNode child = children.get(i);
if (size != sizeOfTree(child)) {
goodNode = false;
}
sum += sizeOfTree(child);
}
if (goodNode) {
count++;
}
sum++;
node.size = sum;
return sum;
}
private static class TNode {
int val;
int size;
List<TNode> children;
TNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.size = -1;
this.children = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
}

