LeetCode-in-Java
3245. Alternating Groups III
Hard
There are some red and blue tiles arranged circularly. You are given an array of integers colors and a 2D integers array queries.
The color of tile i is represented by colors[i]:
colors[i] == 0means that tileiis red.colors[i] == 1means that tileiis blue.
An alternating group is a contiguous subset of tiles in the circle with alternating colors (each tile in the group except the first and last one has a different color from its adjacent tiles in the group).
You have to process queries of two types:
queries[i] = [1, sizei], determine the count of alternating groups with sizesizei.queries[i] = [2, indexi, colori], changecolors[indexi]tocolori.
Return an array answer containing the results of the queries of the first type in order.
Note that since colors represents a circle, the first and the last tiles are considered to be next to each other.
Example 1:
Input: colors = [0,1,1,0,1], queries = [[2,1,0],[1,4]]
Output: [2]
Explanation:
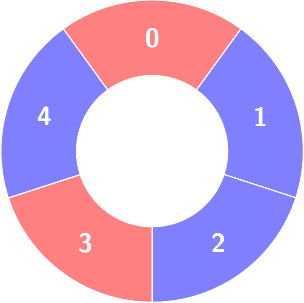
First query:
Change colors[1] to 0.
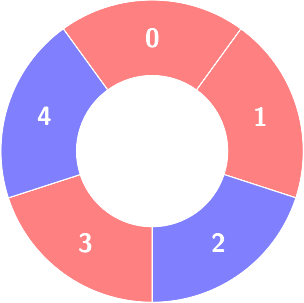
Second query:
Count of the alternating groups with size 4:
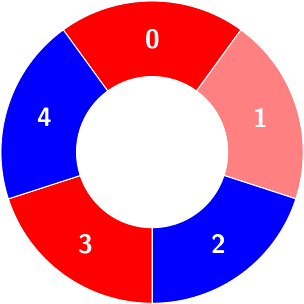
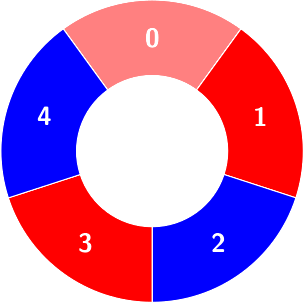
Example 2:
Input: colors = [0,0,1,0,1,1], queries = [[1,3],[2,3,0],[1,5]]
Output: [2,0]
Explanation:
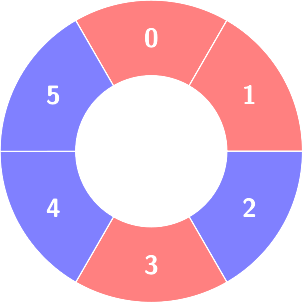
First query:
Count of the alternating groups with size 3:
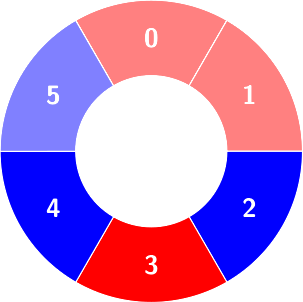
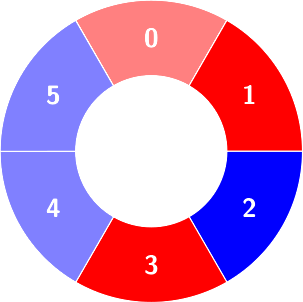
Second query: colors will not change.
Third query: There is no alternating group with size 5.
Constraints:
4 <= colors.length <= 5 * 1040 <= colors[i] <= 11 <= queries.length <= 5 * 104queries[i][0] == 1orqueries[i][0] == 2- For all
ithat:queries[i][0] == 1:queries[i].length == 2,3 <= queries[i][1] <= colors.length - 1queries[i][0] == 2:queries[i].length == 3,0 <= queries[i][1] <= colors.length - 1,0 <= queries[i][2] <= 1
Solution
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.BitSet;
import java.util.List;
public class Solution {
public List<Integer> numberOfAlternatingGroups(int[] colors, int[][] queries) {
int n = colors.length;
BitSet set = new BitSet();
BIT bit = new BIT(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (colors[i] == colors[getIndex(i + 1, n)]) {
add(set, bit, n, i);
}
}
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] q : queries) {
if (q[0] == 1) {
if (set.isEmpty()) {
ans.add(n);
} else {
int size = q[1];
int[] res = bit.query(size);
ans.add(res[1] - res[0] * (size - 1));
}
} else {
int i = q[1];
int color = colors[i];
if (q[2] == color) {
continue;
}
int pre = getIndex(i - 1, n);
if (colors[pre] == color) {
remove(set, bit, n, pre);
}
int next = getIndex(i + 1, n);
if (colors[next] == color) {
remove(set, bit, n, i);
}
colors[i] ^= 1;
color = colors[i];
if (colors[pre] == color) {
add(set, bit, n, pre);
}
if (colors[next] == color) {
add(set, bit, n, i);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
private void add(BitSet set, BIT bit, int n, int i) {
if (set.isEmpty()) {
bit.update(n, 1);
} else {
update(set, bit, n, i, 1);
}
set.set(i);
}
private void remove(BitSet set, BIT bit, int n, int i) {
set.clear(i);
if (set.isEmpty()) {
bit.update(n, -1);
} else {
update(set, bit, n, i, -1);
}
}
private void update(BitSet set, BIT bit, int n, int i, int v) {
int pre = set.previousSetBit(i);
if (pre == -1) {
pre = set.previousSetBit(n);
}
int next = set.nextSetBit(i);
if (next == -1) {
next = set.nextSetBit(0);
}
bit.update(getIndex(next - pre + n - 1, n) + 1, -v);
bit.update(getIndex(i - pre, n), v);
bit.update(getIndex(next - i, n), v);
}
private int getIndex(int index, int mod) {
int result = index >= mod ? index - mod : index;
return index < 0 ? index + mod : result;
}
private static class BIT {
int n;
int[] tree1;
int[] tree2;
BIT(int n) {
this.n = n + 1;
tree1 = new int[n + 1];
tree2 = new int[n + 1];
}
void update(int size, int v) {
for (int i = size; i > 0; i -= i & -i) {
tree1[i] += v;
tree2[i] += v * size;
}
}
int[] query(int size) {
int count = 0;
int sum = 0;
for (int i = size; i < n; i += i & -i) {
count += tree1[i];
sum += tree2[i];
}
return new int[] {count, sum};
}
}
}

