LeetCode-in-Java
3241. Time Taken to Mark All Nodes
Hard
There exists an undirected tree with n nodes numbered 0 to n - 1. You are given a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ui, vi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ui and vi in the tree.
Initially, all nodes are unmarked. For each node i:
- If
iis odd, the node will get marked at timexif there is at least one node adjacent to it which was marked at timex - 1. - If
iis even, the node will get marked at timexif there is at least one node adjacent to it which was marked at timex - 2.
Return an array times where times[i] is the time when all nodes get marked in the tree, if you mark node i at time t = 0.
Note that the answer for each times[i] is independent, i.e. when you mark node i all other nodes are unmarked.
Example 1:
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2]]
Output: [2,4,3]
Explanation:
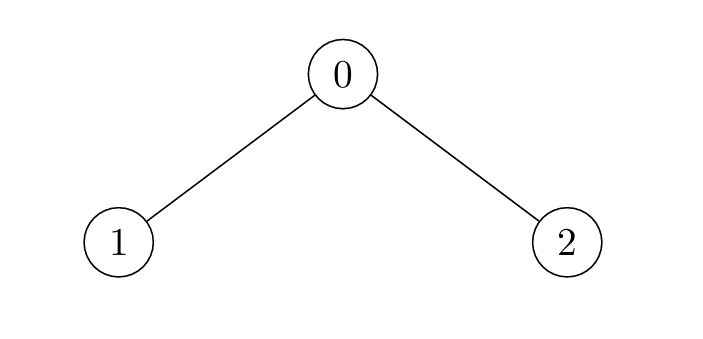
- For
i = 0:- Node 1 is marked at
t = 1, and Node 2 att = 2.
- Node 1 is marked at
- For
i = 1:- Node 0 is marked at
t = 2, and Node 2 att = 4.
- Node 0 is marked at
- For
i = 2:- Node 0 is marked at
t = 2, and Node 1 att = 3.
- Node 0 is marked at
Example 2:
Input: edges = [[0,1]]
Output: [1,2]
Explanation:
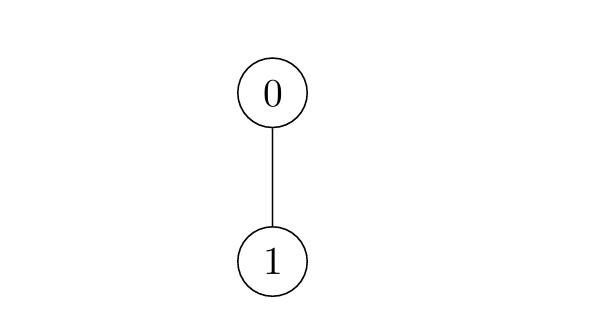
- For
i = 0:- Node 1 is marked at
t = 1.
- Node 1 is marked at
- For
i = 1:- Node 0 is marked at
t = 2.
- Node 0 is marked at
Example 3:
Input: edges = [[2,4],[0,1],[2,3],[0,2]]
Output: [4,6,3,5,5]
Explanation:
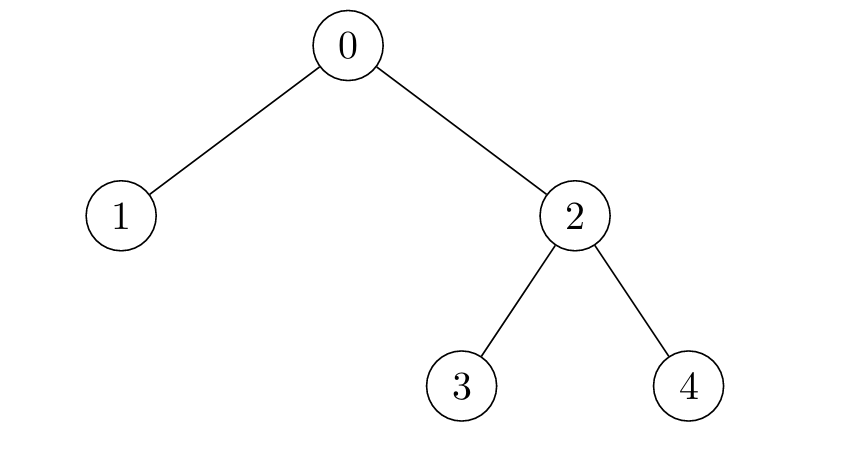
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 105edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= edges[i][0], edges[i][1] <= n - 1- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree.
Solution
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Solution {
private int[] head;
private int[] nxt;
private int[] to;
private int[] last;
private int[] lastNo;
private int[] second;
private int[] ans;
public int[] timeTaken(int[][] edges) {
int n = edges.length + 1;
head = new int[n];
nxt = new int[n << 1];
to = new int[n << 1];
Arrays.fill(head, -1);
int i = 0;
int j = 2;
while (i < edges.length) {
int u = edges[i][0];
int v = edges[i][1];
nxt[j] = head[u];
head[u] = j;
to[j] = v;
j++;
nxt[j] = head[v];
head[v] = j;
to[j] = u;
j++;
i++;
}
last = new int[n];
lastNo = new int[n];
second = new int[n];
ans = new int[n];
dfs(-1, 0);
System.arraycopy(last, 0, ans, 0, n);
dfs2(-1, 0, 0);
return ans;
}
private void dfs2(int f, int u, int preLast) {
int e = head[u];
int v;
while (e != -1) {
v = to[e];
if (f != v) {
int pl;
if (v == lastNo[u]) {
pl = Math.max(preLast, second[u]) + ((u & 1) == 0 ? 2 : 1);
} else {
pl = Math.max(preLast, last[u]) + ((u & 1) == 0 ? 2 : 1);
}
ans[v] = Math.max(ans[v], pl);
dfs2(u, v, pl);
}
e = nxt[e];
}
}
private void dfs(int f, int u) {
int e = head[u];
int v;
while (e != -1) {
v = to[e];
if (f != v) {
dfs(u, v);
int t = last[v] + ((v & 1) == 0 ? 2 : 1);
if (last[u] < t) {
second[u] = last[u];
last[u] = t;
lastNo[u] = v;
} else if (second[u] < t) {
second[u] = t;
}
}
e = nxt[e];
}
}
}

