LeetCode-in-Java
3161. Block Placement Queries
Hard
There exists an infinite number line, with its origin at 0 and extending towards the positive x-axis.
You are given a 2D array queries, which contains two types of queries:
- For a query of type 1,
queries[i] = [1, x]. Build an obstacle at distancexfrom the origin. It is guaranteed that there is no obstacle at distancexwhen the query is asked. - For a query of type 2,
queries[i] = [2, x, sz]. Check if it is possible to place a block of sizeszanywhere in the range[0, x]on the line, such that the block entirely lies in the range[0, x]. A block cannot be placed if it intersects with any obstacle, but it may touch it. Note that you do not actually place the block. Queries are separate.
Return a boolean array results, where results[i] is true if you can place the block specified in the ith query of type 2, and false otherwise.
Example 1:
Input: queries = [[1,2],[2,3,3],[2,3,1],[2,2,2]]
Output: [false,true,true]
Explanation:
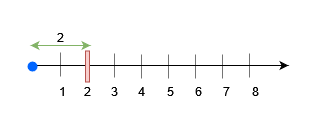
For query 0, place an obstacle at x = 2. A block of size at most 2 can be placed before x = 3.
Example 2:
Input: queries = [[1,7],[2,7,6],[1,2],[2,7,5],[2,7,6]]
Output: [true,true,false]
Explanation:
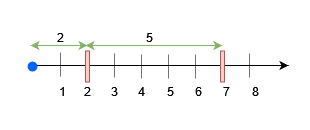
- Place an obstacle at
x = 7for query 0. A block of size at most 7 can be placed beforex = 7. - Place an obstacle at
x = 2for query 2. Now, a block of size at most 5 can be placed beforex = 7, and a block of size at most 2 beforex = 2.
Constraints:
1 <= queries.length <= 15 * 1042 <= queries[i].length <= 31 <= queries[i][0] <= 21 <= x, sz <= min(5 * 104, 3 * queries.length)- The input is generated such that for queries of type 1, no obstacle exists at distance
xwhen the query is asked. - The input is generated such that there is at least one query of type 2.
Solution
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class Solution {
public List<Boolean> getResults(int[][] queries) {
int m = queries.length;
int[] pos = new int[m + 1];
int size = 0;
pos[size++] = 0;
int max = 0;
for (int[] q : queries) {
max = Math.max(max, q[1]);
if (q[0] == 1) {
pos[size++] = q[1];
}
}
Arrays.sort(pos, 0, size);
max++;
UnionFind left = new UnionFind(max + 1);
UnionFind right = new UnionFind(max + 1);
BIT bit = new BIT(max);
initializePositions(size, pos, bit, left, right, max);
return List.of(getBooleans(queries, m, size, left, right, bit));
}
private void initializePositions(
int size, int[] pos, BIT bit, UnionFind left, UnionFind right, int max) {
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
int pre = pos[i - 1];
int cur = pos[i];
bit.update(cur, cur - pre);
for (int j = pre + 1; j < cur; j++) {
left.parent[j] = pre;
right.parent[j] = cur;
}
}
for (int j = pos[size - 1] + 1; j < max; j++) {
left.parent[j] = pos[size - 1];
right.parent[j] = max;
}
}
private Boolean[] getBooleans(
int[][] queries, int m, int size, UnionFind left, UnionFind right, BIT bit) {
Boolean[] ans = new Boolean[m - size + 1];
int index = ans.length - 1;
for (int i = m - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
int[] q = queries[i];
int x = q[1];
int pre = left.find(x - 1);
if (q[0] == 1) {
int next = right.find(x + 1);
left.parent[x] = pre;
right.parent[x] = next;
bit.update(next, next - pre);
} else {
int maxGap = Math.max(bit.query(pre), x - pre);
ans[index--] = maxGap >= q[2];
}
}
return ans;
}
private static final class BIT {
int n;
int[] tree;
public BIT(int n) {
this.n = n;
tree = new int[n];
}
public void update(int i, int v) {
while (i < n) {
tree[i] = Math.max(tree[i], v);
i += i & -i;
}
}
public int query(int i) {
int result = 0;
while (i > 0) {
result = Math.max(result, tree[i]);
i &= i - 1;
}
return result;
}
}
private static final class UnionFind {
private final int[] parent;
public UnionFind(int n) {
parent = new int[n];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
public int find(int x) {
if (parent[x] != x) {
parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
}
return parent[x];
}
}
}

