LeetCode-in-Java
2846. Minimum Edge Weight Equilibrium Queries in a Tree
Hard
There is an undirected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1. You are given the integer n and a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ui, vi, wi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ui and vi with weight wi in the tree.
You are also given a 2D integer array queries of length m, where queries[i] = [ai, bi]. For each query, find the minimum number of operations required to make the weight of every edge on the path from ai to bi equal. In one operation, you can choose any edge of the tree and change its weight to any value.
Note that:
- Queries are independent of each other, meaning that the tree returns to its initial state on each new query.
- The path from
aitobiis a sequence of distinct nodes starting with nodeaiand ending with nodebisuch that every two adjacent nodes in the sequence share an edge in the tree.
Return an array answer of length m where answer[i] is the answer to the ith query.
Example 1:
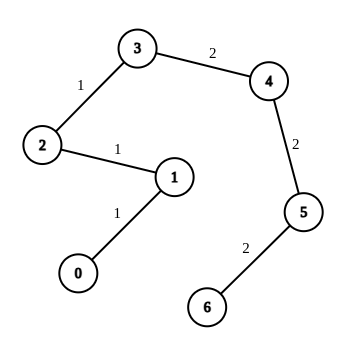
Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1,1],[1,2,1],[2,3,1],[3,4,2],[4,5,2],[5,6,2]], queries = [[0,3],[3,6],[2,6],[0,6]]
Output: [0,0,1,3]
Explanation: In the first query, all the edges in the path from 0 to 3 have a weight of 1. Hence, the answer is 0.
In the second query, all the edges in the path from 3 to 6 have a weight of 2. Hence, the answer is 0. In the third query, we change the weight of edge [2,3] to 2. After this operation, all the edges in the path from 2 to 6 have a weight of 2. Hence, the answer is 1.
In the fourth query, we change the weights of edges [0,1], [1,2] and [2,3] to 2. After these operations, all the edges in the path from 0 to 6 have a weight of 2. Hence, the answer is 3. For each queries[i], it can be shown that answer[i] is the minimum number of operations needed to equalize all the edge weights in the path from ai to bi.
Example 2:
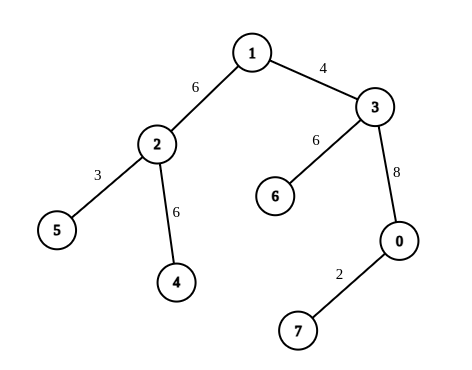
Input: n = 8, edges = [[1,2,6],[1,3,4],[2,4,6],[2,5,3],[3,6,6],[3,0,8],[7,0,2]], queries = [[4,6],[0,4],[6,5],[7,4]]
Output: [1,2,2,3]
Explanation: In the first query, we change the weight of edge [1,3] to 6. After this operation, all the edges in the path from 4 to 6 have a weight of 6. Hence, the answer is 1.
In the second query, we change the weight of edges [0,3] and [3,1] to 6. After these operations, all the edges in the path from 0 to 4 have a weight of 6. Hence, the answer is 2.
In the third query, we change the weight of edges [1,3] and [5,2] to 6. After these operations, all the edges in the path from 6 to 5 have a weight of 6. Hence, the answer is 2.
In the fourth query, we change the weights of edges [0,7], [0,3] and [1,3] to 6. After these operations, all the edges in the path from 7 to 4 have a weight of 6. Hence, the answer is 3. For each queries[i], it can be shown that answer[i] is the minimum number of operations needed to equalize all the edge weights in the path from ai to bi.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 104edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 30 <= ui, vi < n1 <= wi <= 26- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree. 1 <= queries.length == m <= 2 * 104queries[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < n
Solution
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
@SuppressWarnings("java:S107")
public class Solution {
private static class Node {
int v;
int w;
Node(int v, int w) {
this.v = v;
this.w = w;
}
}
public int[] minOperationsQueries(int n, int[][] edges, int[][] queries) {
List<List<Node>> graph = createGraph(edges, n);
int queryCount = queries.length;
int[] res = new int[queryCount];
int[] parent = new int[n];
int[] level = new int[n];
int[][] weightFreq = new int[n][27];
int[] freq = new int[27];
int height = (int) (Math.log(n) / Math.log(2)) + 1;
int[][] up = new int[n][height];
for (int[] arr : up) {
Arrays.fill(arr, -1);
}
dfs(graph, 0, 0, -1, parent, level, weightFreq, freq);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
up[i][0] = parent[i];
}
for (int i = 1; i < height; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (up[j][i - 1] == -1) {
up[j][i] = -1;
continue;
}
up[j][i] = up[up[j][i - 1]][i - 1];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < queryCount; i++) {
int src = queries[i][0];
int dest = queries[i][1];
int lcaNode = lca(src, dest, up, height, level);
res[i] = processResult(weightFreq[src], weightFreq[dest], weightFreq[lcaNode]);
}
return res;
}
private int lca(int src, int dest, int[][] up, int height, int[] level) {
int curr1 = src;
int curr2 = dest;
int minlevel;
if (level[curr1] > level[curr2]) {
minlevel = level[curr2];
curr1 = getKthAncestor(curr1, level[curr1] - level[curr2], up, height);
} else if (level[curr1] <= level[curr2]) {
minlevel = level[curr1];
curr2 = getKthAncestor(curr2, level[curr2] - level[curr1], up, height);
} else {
minlevel = level[curr1];
}
if (curr1 == curr2) {
return curr1;
}
int l = 0;
int h = level[curr2];
while (l <= h) {
int mid = l + (h - l) / 2;
int p1 = getKthAncestor(curr1, minlevel - mid, up, height);
int p2 = getKthAncestor(curr2, minlevel - mid, up, height);
if (p1 == p2) {
l = mid + 1;
} else {
h = mid - 1;
}
}
return getKthAncestor(curr1, minlevel - l + 1, up, height);
}
private int getKthAncestor(int node, int k, int[][] up, int height) {
int curr = node;
for (int i = 0; i < height && k >> i != 0; i++) {
if (((1 << i) & k) != 0) {
if (curr == -1) {
return -1;
}
curr = up[curr][i];
}
}
return curr;
}
private int processResult(int[] freqSrc, int[] freqDest, int[] freqLCA) {
int[] freqPath = new int[27];
for (int i = 1; i < 27; i++) {
freqPath[i] = freqSrc[i] + freqDest[i] - 2 * freqLCA[i];
}
int max = 0;
int pathlen = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < 27; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, freqPath[i]);
pathlen += freqPath[i];
}
return pathlen - max;
}
private void dfs(
List<List<Node>> graph,
int src,
int currlevel,
int p,
int[] parent,
int[] level,
int[][] weightFreq,
int[] freq) {
parent[src] = p;
level[src] = currlevel;
System.arraycopy(freq, 0, weightFreq[src], 0, freq.length);
for (Node node : graph.get(src)) {
int v = node.v;
int w = node.w;
if (v != p) {
freq[w]++;
dfs(graph, v, currlevel + 1, src, parent, level, weightFreq, freq);
freq[w]--;
}
}
}
private List<List<Node>> createGraph(int[][] edges, int n) {
List<List<Node>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int[] edge : edges) {
int u = edge[0];
int v = edge[1];
int w = edge[2];
graph.get(u).add(new Node(v, w));
graph.get(v).add(new Node(u, w));
}
return graph;
}
}

