LeetCode-in-Java
2493. Divide Nodes Into the Maximum Number of Groups
Hard
You are given a positive integer n representing the number of nodes in an undirected graph. The nodes are labeled from 1 to n.
You are also given a 2D integer array edges, where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is a bidirectional edge between nodes ai and bi. Notice that the given graph may be disconnected.
Divide the nodes of the graph into m groups (1-indexed) such that:
- Each node in the graph belongs to exactly one group.
- For every pair of nodes in the graph that are connected by an edge
[ai, bi], ifaibelongs to the group with indexx, andbibelongs to the group with indexy, then|y - x| = 1.
Return the maximum number of groups (i.e., maximum m) into which you can divide the nodes. Return -1 if it is impossible to group the nodes with the given conditions.
Example 1:
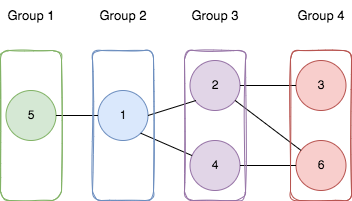
Input: n = 6, edges = [[1,2],[1,4],[1,5],[2,6],[2,3],[4,6]]
Output: 4
Explanation: As shown in the image we:
- Add node 5 to the first group.
- Add node 1 to the second group.
- Add nodes 2 and 4 to the third group.
- Add nodes 3 and 6 to the fourth group.
We can see that every edge is satisfied. It can be shown that that if we create a fifth group and move any node from the third or fourth group to it, at least on of the edges will not be satisfied.
Example 2:
Input: n = 3, edges = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,1]]
Output: -1
Explanation: If we add node 1 to the first group, node 2 to the second group, and node 3 to the third group to satisfy the first two edges, we can see that the third edge will not be satisfied. It can be shown that no grouping is possible.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 5001 <= edges.length <= 104edges[i].length == 21 <= ai, bi <= nai != bi- There is at most one edge between any pair of vertices.
Solution
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Solution {
public int magnificentSets(int n, int[][] edges) {
List<List<Integer>> adj = new ArrayList<>();
int[] visited = new int[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(visited, -1);
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int[] edge : edges) {
adj.get(edge[0]).add(edge[1]);
adj.get(edge[1]).add(edge[0]);
}
int[] comp = new int[n + 1];
int count = -1;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (visited[i] == -1) {
count++;
comp[count] = bfs(i, adj, visited, count, n);
if (comp[count] == -1) {
return -1;
}
} else {
comp[visited[i]] = Math.max(comp[visited[i]], bfs(i, adj, visited, visited[i], n));
}
}
for (int group : comp) {
ans += group;
}
return ans;
}
private int bfs(int start, List<List<Integer>> adj, int[] visited, int count, int n) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
visited[start] = count;
int ans = 1;
int[] group = new int[n + 1];
q.add(start);
group[start] = 1;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int node = q.remove();
for (int adjN : adj.get(node)) {
if (group[adjN] == 0) {
visited[adjN] = count;
group[adjN] = group[node] + 1;
q.add(adjN);
ans = Math.max(ans, group[adjN]);
} else if (Math.abs(group[adjN] - group[node]) != 1) {
return -1;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}

