LeetCode-in-Java
2415. Reverse Odd Levels of Binary Tree
Medium
Given the root of a perfect binary tree, reverse the node values at each odd level of the tree.
- For example, suppose the node values at level 3 are
[2,1,3,4,7,11,29,18], then it should become[18,29,11,7,4,3,1,2].
Return the root of the reversed tree.
A binary tree is perfect if all parent nodes have two children and all leaves are on the same level.
The level of a node is the number of edges along the path between it and the root node.
Example 1:
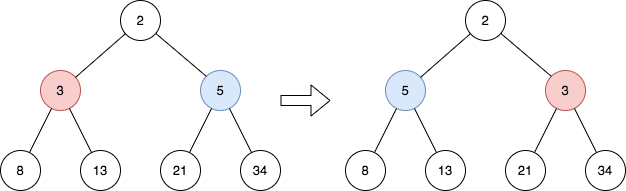
Input: root = [2,3,5,8,13,21,34]
Output: [2,5,3,8,13,21,34]
Explanation:
The tree has only one odd level.
The nodes at level 1 are 3, 5 respectively, which are reversed and become 5, 3.
Example 2:
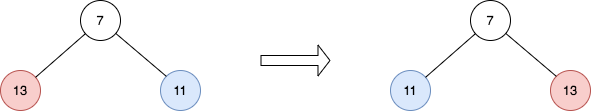
Input: root = [7,13,11]
Output: [7,11,13]
Explanation:
The nodes at level 1 are 13, 11, which are reversed and become 11, 13.
Example 3:
Input: root = [0,1,2,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,2,2,2,2]
Output: [0,2,1,0,0,0,0,2,2,2,2,1,1,1,1]
Explanation:
The odd levels have non-zero values.
The nodes at level 1 were 1, 2, and are 2, 1 after the reversal.
The nodes at level 3 were 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, and are 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1 after the reversal.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 214]. 0 <= Node.val <= 105rootis a perfect binary tree.
Solution
import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
/*
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
private List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public TreeNode reverseOddLevels(TreeNode root) {
solve(root);
return enrich(list, 0);
}
private TreeNode enrich(List<Integer> list, int i) {
TreeNode root = null;
if (i < list.size()) {
root = new TreeNode(list.get(i));
root.left = enrich(list, 2 * i + 1);
root.right = enrich(list, 2 * i + 2);
}
return root;
}
private void solve(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
int level = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode cur = q.remove();
res.add(cur.val);
if (cur.left != null) {
q.add(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
q.add(cur.right);
}
}
if (level % 2 != 0) {
for (int i = res.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
list.add(res.get(i));
}
} else {
list.addAll(res);
}
level++;
}
}
}

