LeetCode-in-Java
2280. Minimum Lines to Represent a Line Chart
Medium
You are given a 2D integer array stockPrices where stockPrices[i] = [dayi, pricei] indicates the price of the stock on day dayi is pricei. A line chart is created from the array by plotting the points on an XY plane with the X-axis representing the day and the Y-axis representing the price and connecting adjacent points. One such example is shown below:
Return the minimum number of lines needed to represent the line chart.
Example 1:
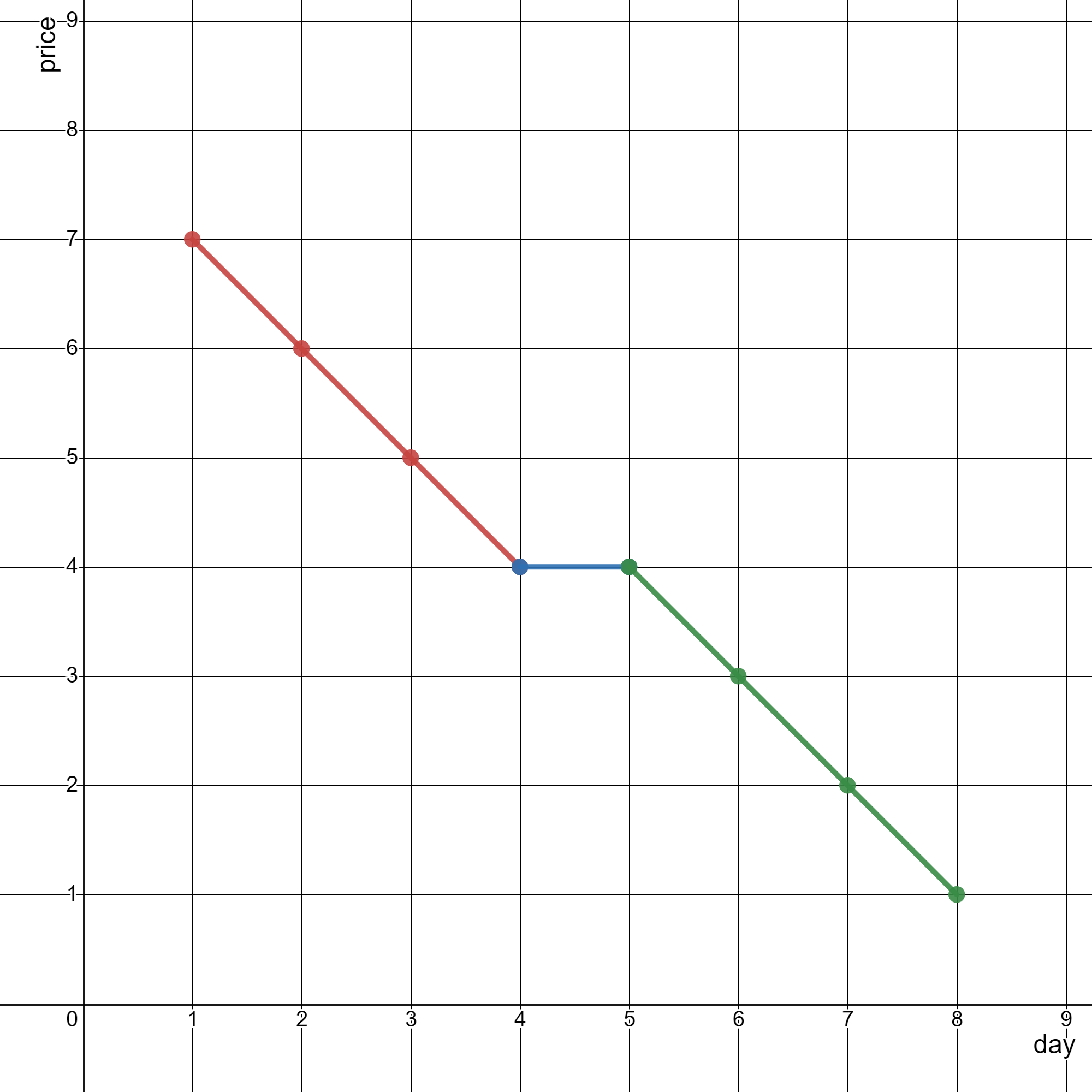
Input: stockPrices = [[1,7],[2,6],[3,5],[4,4],[5,4],[6,3],[7,2],[8,1]]
Output: 3
Explanation:
The diagram above represents the input, with the X-axis representing the day and Y-axis representing the price.
The following 3 lines can be drawn to represent the line chart:
-
Line 1 (in red) from (1,7) to (4,4) passing through (1,7), (2,6), (3,5), and (4,4).
-
Line 2 (in blue) from (4,4) to (5,4).
-
Line 3 (in green) from (5,4) to (8,1) passing through (5,4), (6,3), (7,2), and (8,1).
It can be shown that it is not possible to represent the line chart using less than 3 lines.
Example 2:
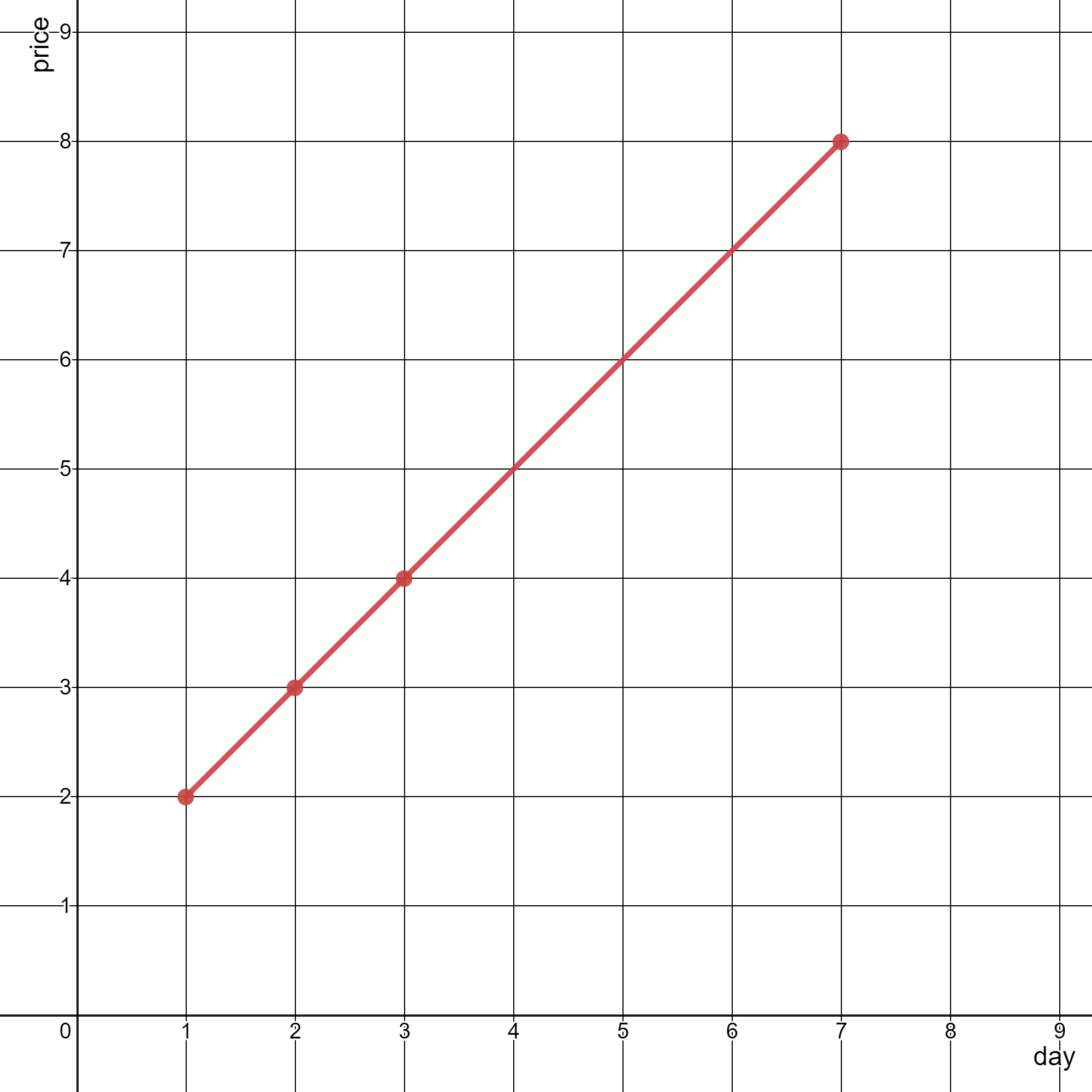
Input: stockPrices = [[3,4],[1,2],[7,8],[2,3]]
Output: 1
Explanation: As shown in the diagram above, the line chart can be represented with a single line.
Constraints:
1 <= stockPrices.length <= 105stockPrices[i].length == 21 <= dayi, pricei <= 109- All
dayiare distinct.
Solution
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Solution {
public int minimumLines(int[][] stockPrices) {
if (stockPrices.length == 1) {
return 0;
}
Arrays.sort(stockPrices, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
// multiply with 1.0 to make it double and multiply with 100 for making it big so that
// difference won't come out to be very less and after division it become 0.
// failing for one of the case without multiply 100
double lastSlope =
(stockPrices[1][1] - stockPrices[0][1])
* 100
/ ((stockPrices[1][0] - stockPrices[0][0]) * 1.0);
int ans = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < stockPrices.length; i++) {
double curSlope =
(stockPrices[i][1] - stockPrices[i - 1][1])
* 100
/ ((stockPrices[i][0] - stockPrices[i - 1][0]) * 1.0);
if (lastSlope != curSlope) {
lastSlope = curSlope;
ans++;
}
}
return ans;
}
}

