LeetCode-in-Java
2251. Number of Flowers in Full Bloom
Hard
You are given a 0-indexed 2D integer array flowers, where flowers[i] = [starti, endi] means the ith flower will be in full bloom from starti to endi (inclusive). You are also given a 0-indexed integer array persons of size n, where persons[i] is the time that the ith person will arrive to see the flowers.
Return an integer array answer of size n, where answer[i] is the number of flowers that are in full bloom when the ith person arrives.
Example 1:
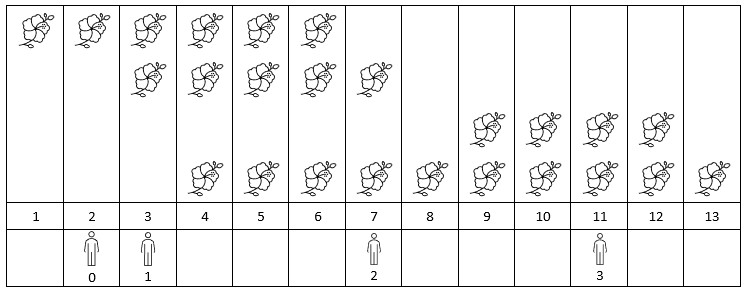
Input: flowers = [[1,6],[3,7],[9,12],[4,13]], persons = [2,3,7,11]
Output: [1,2,2,2]
Explanation: The figure above shows the times when the flowers are in full bloom and when the people arrive. For each person, we return the number of flowers in full bloom during their arrival.
Example 2:
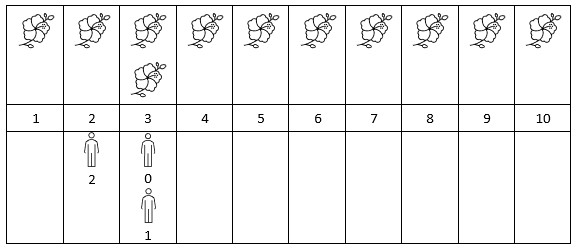
Input: flowers = [[1,10],[3,3]], persons = [3,3,2]
Output: [2,2,1]
Explanation: The figure above shows the times when the flowers are in full bloom and when the people arrive. For each person, we return the number of flowers in full bloom during their arrival.
Constraints:
1 <= flowers.length <= 5 * 104flowers[i].length == 21 <= starti <= endi <= 1091 <= persons.length <= 5 * 1041 <= persons[i] <= 109
Solution
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
@SuppressWarnings("java:S135")
public class Solution {
public int[] fullBloomFlowers(int[][] flowers, int[] persons) {
Arrays.sort(flowers, Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));
int[] ans = new int[persons.length];
PriorityQueue<Pair> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a.j));
int j = 0;
int[][] t = new int[persons.length][2];
for (int i = 0; i < persons.length; i++) {
t[i][0] = persons[i];
t[i][1] = i;
}
Arrays.sort(t, Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));
for (int[] ints : t) {
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
if (pq.peek().j < ints[0]) {
pq.poll();
} else {
break;
}
}
while (j < flowers.length) {
if (flowers[j][0] <= ints[0] && flowers[j][1] >= ints[0]) {
pq.add(new Pair(flowers[j][0], flowers[j][1]));
j++;
continue;
}
if (flowers[j][1] < ints[0]) {
j++;
continue;
}
break;
}
ans[ints[1]] = pq.size();
}
return ans;
}
private static class Pair {
int i;
int j;
Pair(int i, int j) {
this.i = i;
this.j = j;
}
}
}

