LeetCode-in-Java
1932. Merge BSTs to Create Single BST
Hard
You are given n BST (binary search tree) root nodes for n separate BSTs stored in an array trees (0-indexed). Each BST in trees has at most 3 nodes, and no two roots have the same value. In one operation, you can:
- Select two distinct indices
iandjsuch that the value stored at one of the leaves oftrees[i]is equal to the root value oftrees[j]. - Replace the leaf node in
trees[i]withtrees[j]. - Remove
trees[j]fromtrees.
Return the root of the resulting BST if it is possible to form a valid BST after performing n - 1 operations, or null if it is impossible to create a valid BST.
A BST (binary search tree) is a binary tree where each node satisfies the following property:
- Every node in the node’s left subtree has a value strictly less than the node’s value.
- Every node in the node’s right subtree has a value strictly greater than the node’s value.
A leaf is a node that has no children.
Example 1:
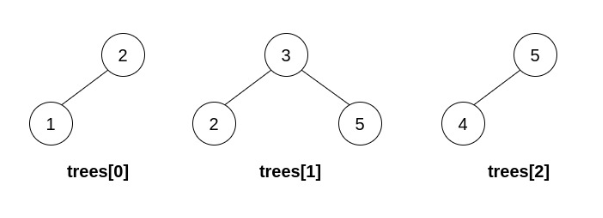
Input: trees = [[2,1],[3,2,5],[5,4]]
Output: [3,2,5,1,null,4]
Explanation: In the first operation, pick i=1 and j=0, and merge trees[0] into trees[1]. Delete trees[0], so trees = [[3,2,5,1],[5,4]]. 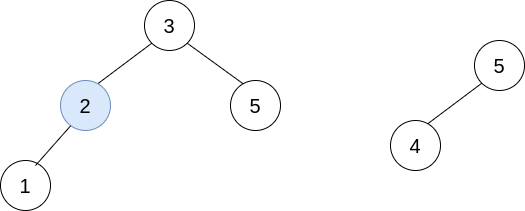 In the second operation, pick i=0 and j=1, and merge trees[1] into trees[0]. Delete trees[1], so trees = [[3,2,5,1,null,4]].
In the second operation, pick i=0 and j=1, and merge trees[1] into trees[0]. Delete trees[1], so trees = [[3,2,5,1,null,4]]. 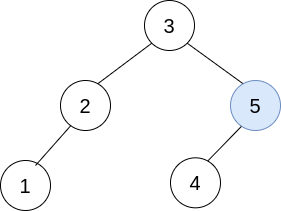 The resulting tree, shown above, is a valid BST, so return its root.
The resulting tree, shown above, is a valid BST, so return its root.
Example 2:
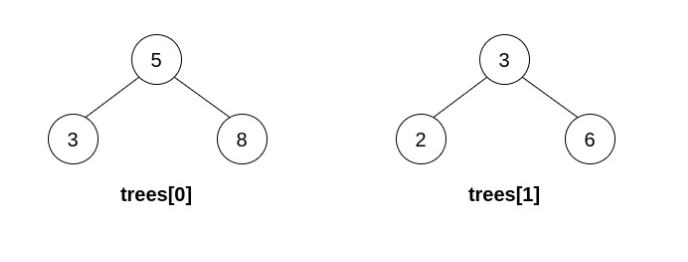
Input: trees = [[5,3,8],[3,2,6]]
Output: []
Explanation: Pick i=0 and j=1 and merge trees[1] into trees[0]. Delete trees[1], so trees = [[5,3,8,2,6]]. 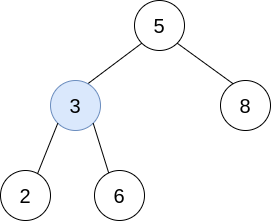 The resulting tree is shown above. This is the only valid operation that can be performed, but the resulting tree is not a valid BST, so return null.
The resulting tree is shown above. This is the only valid operation that can be performed, but the resulting tree is not a valid BST, so return null.
Example 3:
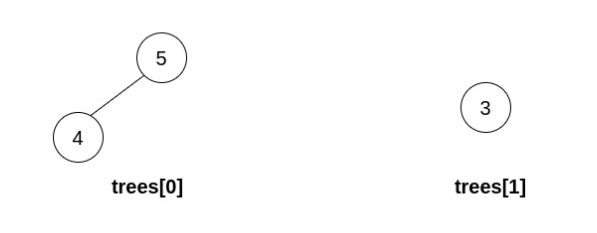
Input: trees = [[5,4],[3]]
Output: []
Explanation: It is impossible to perform any operations.
Constraints:
n == trees.length1 <= n <= 5 * 104- The number of nodes in each tree is in the range
[1, 3]. - Each node in the input may have children but no grandchildren.
- No two roots of
treeshave the same value. - All the trees in the input are valid BSTs.
1 <= TreeNode.val <= 5 * 104.
Solution
import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Solution {
private static final Map<Integer, TreeNode> ROOT_VALS = new HashMap<>();
public TreeNode canMerge(List<TreeNode> trees) {
TreeNode root = findRoot(trees);
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
for (TreeNode t : trees) {
ROOT_VALS.put(t.val, t);
}
bfs(root);
if (!isValidBST(root) || ROOT_VALS.size() != 1) {
return null;
}
return root;
}
private TreeNode findRoot(List<TreeNode> trees) {
TreeNode root = null;
Map<Integer, Integer> valCnts = new HashMap<>();
for (TreeNode t : trees) {
valCnts.put(t.val, valCnts.getOrDefault(t.val, 0) + 1);
if (t.left != null) {
valCnts.put(t.left.val, valCnts.getOrDefault(t.left.val, 0) + 1);
}
if (t.right != null) {
valCnts.put(t.right.val, valCnts.getOrDefault(t.right.val, 0) + 1);
}
}
for (TreeNode t : trees) {
if (valCnts.get(t.val) == 1) {
if (root == null) {
root = t;
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
return root;
}
private void bfs(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode parent = q.poll();
if (parent.left != null && ROOT_VALS.containsKey(parent.left.val)) {
TreeNode toConnect = ROOT_VALS.get(parent.left.val);
ROOT_VALS.remove(toConnect.val);
parent.left = toConnect;
q.offer(parent.left);
}
if (parent.right != null && ROOT_VALS.containsKey(parent.right.val)) {
TreeNode toConnect = ROOT_VALS.get(parent.right.val);
ROOT_VALS.remove(toConnect.val);
parent.right = toConnect;
q.offer(parent.right);
}
}
}
}
private boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
return isValidBST(root, Integer.MIN_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
private boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root, int min, int max) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
if (root.val <= min || root.val >= max) {
return false;
}
return isValidBST(root.left, min, root.val) && isValidBST(root.right, root.val, max);
}
}

