LeetCode-in-Java
1505. Minimum Possible Integer After at Most K Adjacent Swaps On Digits
Hard
You are given a string num representing the digits of a very large integer and an integer k. You are allowed to swap any two adjacent digits of the integer at most k times.
Return the minimum integer you can obtain also as a string.
Example 1:
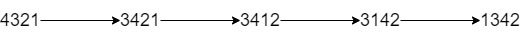
Input: num = “4321”, k = 4
Output: “1342”
Explanation: The steps to obtain the minimum integer from 4321 with 4 adjacent swaps are shown.
Example 2:
Input: num = “100”, k = 1
Output: “010”
Explanation: It’s ok for the output to have leading zeros, but the input is guaranteed not to have any leading zeros.
Example 3:
Input: num = “36789”, k = 1000
Output: “36789”
Explanation: We can keep the number without any swaps.
Constraints:
1 <= num.length <= 3 * 104numconsists of only digits and does not contain leading zeros.1 <= k <= 104
Solution
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Solution {
public String minInteger(String num, int k) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int[] digitPos = new int[10];
int[] reduceMove = new int[10];
int matchAmount = 0;
char[] chars = num.toCharArray();
Arrays.fill(digitPos, chars.length);
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
int cur = chars[i] - '0';
if (digitPos[cur] == chars.length) {
digitPos[cur] = i;
matchAmount++;
if (matchAmount == 10) {
break;
}
}
}
int curIndex = 0;
while (k > 0 && curIndex < chars.length) {
for (int digit = 0; digit <= 9; digit++) {
if (digitPos[digit] < chars.length && digitPos[digit] - reduceMove[digit] <= k) {
sb.append(chars[digitPos[digit]]);
k -= (digitPos[digit] - reduceMove[digit]);
curIndex++;
reduceMove[digit]++;
for (int j = 0; j <= 9; j++) {
if (j != digit && digitPos[j] > digitPos[digit]) {
reduceMove[j]++;
}
}
boolean find = false;
for (int next = digitPos[digit] + 1; next < chars.length; next++) {
int cur = chars[next] - '0';
if (cur == digit) {
find = true;
digitPos[digit] = next;
break;
}
if (next < digitPos[cur]) {
reduceMove[digit]++;
}
}
if (!find) {
digitPos[digit] = chars.length;
}
break;
}
}
}
int start = Arrays.stream(digitPos).min().getAsInt();
for (int i = start; i < chars.length; i++) {
if (digitPos[chars[i] - '0'] <= i) {
sb.append(chars[i]);
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
}

