LeetCode-in-Java
1478. Allocate Mailboxes
Hard
Given the array houses where houses[i] is the location of the ith house along a street and an integer k, allocate k mailboxes in the street.
Return the minimum total distance between each house and its nearest mailbox.
The test cases are generated so that the answer fits in a 32-bit integer.
Example 1:
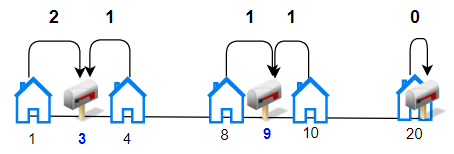
Input: houses = [1,4,8,10,20], k = 3
Output: 5
Explanation: Allocate mailboxes in position 3, 9 and 20. Minimum total distance from each houses to nearest mailboxes is |3-1| + |4-3| + |9-8| + |10-9| + |20-20| = 5
Example 2:
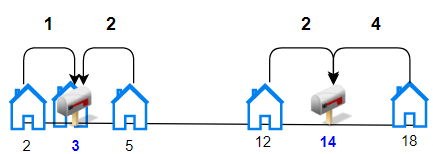
Input: houses = [2,3,5,12,18], k = 2
Output: 9
Explanation: Allocate mailboxes in position 3 and 14. Minimum total distance from each houses to nearest mailboxes is |2-3| + |3-3| + |5-3| + |12-14| + |18-14| = 9.
Constraints:
1 <= k <= houses.length <= 1001 <= houses[i] <= 104- All the integers of
housesare unique.
Solution
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Solution {
public int minDistance(int[] houses, int k) {
Arrays.sort(houses);
int n = houses.length;
int[][] dp = new int[n][k + 1];
for (int[] ar : dp) {
Arrays.fill(ar, -1);
}
return recur(houses, 0, k, dp);
}
private int recur(int[] houses, int idx, int k, int[][] dp) {
if (dp[idx][k] != -1) {
return dp[idx][k];
}
if (k == 1) {
int dist = calDist(houses, idx, houses.length - 1);
dp[idx][k] = dist;
return dp[idx][k];
}
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = idx; i + k - 1 < houses.length; i++) {
int dist = calDist(houses, idx, i);
dist += recur(houses, i + 1, k - 1, dp);
min = Math.min(min, dist);
}
dp[idx][k] = min;
return min;
}
private int calDist(int[] ar, int start, int end) {
int result = 0;
while (start < end) {
result += ar[end--] - ar[start++];
}
return result;
}
}

