LeetCode-in-Java
1457. Pseudo-Palindromic Paths in a Binary Tree
Medium
Given a binary tree where node values are digits from 1 to 9. A path in the binary tree is said to be pseudo-palindromic if at least one permutation of the node values in the path is a palindrome.
Return the number of pseudo-palindromic paths going from the root node to leaf nodes.
Example 1:
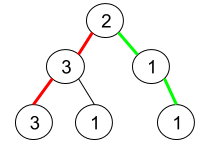
Input: root = [2,3,1,3,1,null,1]
Output: 2
Explanation: The figure above represents the given binary tree. There are three paths going from the root node to leaf nodes: the red path [2,3,3], the green path [2,1,1], and the path [2,3,1]. Among these paths only red path and green path are pseudo-palindromic paths since the red path [2,3,3] can be rearranged in [3,2,3] (palindrome) and the green path [2,1,1] can be rearranged in [1,2,1] (palindrome).
Example 2:
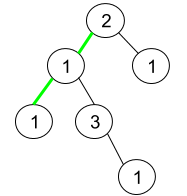
Input: root = [2,1,1,1,3,null,null,null,null,null,1]
Output: 1
Explanation: The figure above represents the given binary tree. There are three paths going from the root node to leaf nodes: the green path [2,1,1], the path [2,1,3,1], and the path [2,1]. Among these paths only the green path is pseudo-palindromic since [2,1,1] can be rearranged in [1,2,1] (palindrome).
Example 3:
Input: root = [9]
Output: 1
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 105]. 1 <= Node.val <= 9
Solution
import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode;
/*
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
private int ans;
private int[] arr;
public int pseudoPalindromicPaths(TreeNode root) {
ans = 0;
arr = new int[10];
path(root);
return ans;
}
private int isPalidrome() {
int c = 0;
int s = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
s += arr[i];
if (arr[i] % 2 != 0) {
c++;
}
}
if (s % 2 == 0) {
return c == 0 ? 1 : 0;
}
return c <= 1 ? 1 : 0;
}
private void path(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
arr[root.val]++;
ans += isPalidrome();
arr[root.val]--;
return;
}
arr[root.val]++;
path(root.left);
path(root.right);
arr[root.val]--;
}
}

