LeetCode-in-Java
1329. Sort the Matrix Diagonally
Medium
A matrix diagonal is a diagonal line of cells starting from some cell in either the topmost row or leftmost column and going in the bottom-right direction until reaching the matrix’s end. For example, the matrix diagonal starting from mat[2][0], where mat is a 6 x 3 matrix, includes cells mat[2][0], mat[3][1], and mat[4][2].
Given an m x n matrix mat of integers, sort each matrix diagonal in ascending order and return the resulting matrix.
Example 1:
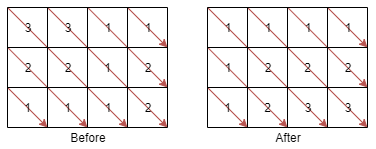
Input: mat = [[3,3,1,1],[2,2,1,2],[1,1,1,2]]
Output: [[1,1,1,1],[1,2,2,2],[1,2,3,3]]
Example 2:
Input: mat = [[11,25,66,1,69,7],[23,55,17,45,15,52],[75,31,36,44,58,8],[22,27,33,25,68,4],[84,28,14,11,5,50]]
Output: [[5,17,4,1,52,7],[11,11,25,45,8,69],[14,23,25,44,58,15],[22,27,31,36,50,66],[84,28,75,33,55,68]]
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1001 <= mat[i][j] <= 100
Solution
public class Solution {
private int[] count = new int[101];
private int m;
private int n;
public void search(int[][] mat, int i, int j) {
for (int ti = i, tj = j; ti < m && tj < n; ti++, tj++) {
count[mat[ti][tj]]++;
}
int c = 0;
for (int ti = i, tj = j; ti < m && tj < n; ti++, tj++) {
while (count[c] == 0) {
c++;
}
mat[ti][tj] = c;
count[c]--;
}
}
public int[][] diagonalSort(int[][] mat) {
m = mat.length;
n = mat[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
search(mat, i, 0);
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
search(mat, 0, i);
}
return mat;
}
}

