LeetCode-in-Java
637. Average of Levels in Binary Tree
Easy
Given the root of a binary tree, return the average value of the nodes on each level in the form of an array. Answers within 10-5 of the actual answer will be accepted.
Example 1:
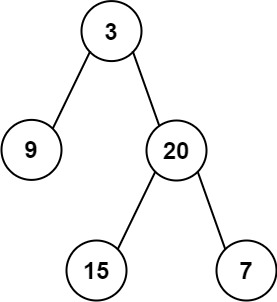
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [3.00000,14.50000,11.00000] Explanation: The average value of nodes on level 0 is 3, on level 1 is 14.5, and on level 2 is 11. Hence return [3, 14.5, 11].
Example 2:
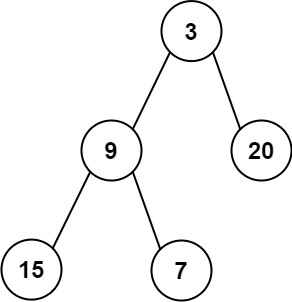
Input: root = [3,9,20,15,7]
Output: [3.00000,14.50000,11.00000]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
Solution
import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/*
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public List<Double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {
Map<Integer, Double[]> map = new HashMap<>();
helper(root, map, 0);
List<Double> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (Double[] pair : map.values()) {
double avg = pair[1] / pair[0];
result.add(avg);
}
return result;
}
private void helper(TreeNode root, Map<Integer, Double[]> map, int level) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Double[] pair = map.containsKey(level) ? map.get(level) : new Double[] {0.0, 0.0};
pair[0] += 1;
pair[1] += root.val;
map.put(level, pair);
helper(root.left, map, level + 1);
helper(root.right, map, level + 1);
}
}

