LeetCode-in-Java
542. 01 Matrix
Medium
Given an m x n binary matrix mat, return the distance of the nearest 0 for each cell.
The distance between two adjacent cells is 1.
Example 1:
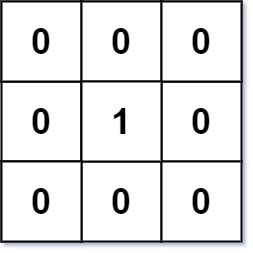
Input: mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
Output: [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
Example 2:
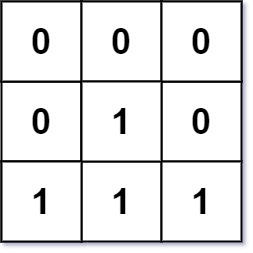
Input: mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,1,1]]
Output: [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,2,1]]
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1041 <= m * n <= 104mat[i][j]is either0or1.- There is at least one
0inmat.
Solution
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Solution {
public int[][] updateMatrix(int[][] mat) {
int[][] dist = new int[mat.length][mat[0].length];
for (int i = 0; i < mat.length; i++) {
Arrays.fill(dist[i], Integer.MAX_VALUE - 100000);
}
for (int i = 0; i < mat.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < mat[0].length; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] == 0) {
dist[i][j] = 0;
} else {
if (i > 0) {
dist[i][j] = Math.min(dist[i][j], dist[i - 1][j] + 1);
}
if (j > 0) {
dist[i][j] = Math.min(dist[i][j], dist[i][j - 1] + 1);
}
}
}
}
for (int i = mat.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = mat[0].length - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (i < mat.length - 1) {
dist[i][j] = Math.min(dist[i][j], dist[i + 1][j] + 1);
}
if (j < mat[0].length - 1) {
dist[i][j] = Math.min(dist[i][j], dist[i][j + 1] + 1);
}
}
}
return dist;
}
}

