LeetCode-in-Java
230. Kth Smallest Element in a BST
Medium
Given the root of a binary search tree, and an integer k, return the kth smallest value (1-indexed) of all the values of the nodes in the tree.
Example 1:
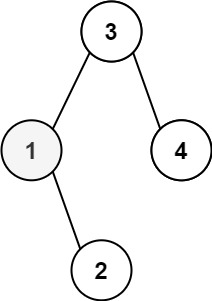
Input: root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1
Output: 1
Example 2:
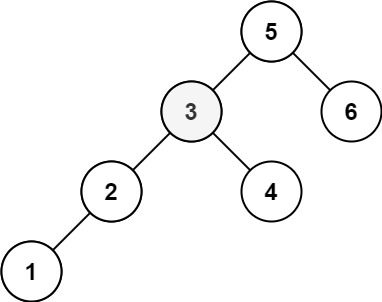
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3
Output: 3
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is
n. 1 <= k <= n <= 1040 <= Node.val <= 104
Follow up: If the BST is modified often (i.e., we can do insert and delete operations) and you need to find the kth smallest frequently, how would you optimize?
Solution
import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode;
/*
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
private int k;
private int count = 0;
private int val;
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
this.k = k;
calculate(root);
return val;
}
private void calculate(TreeNode node) {
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
count++;
if (count == k) {
this.val = node.val;
}
return;
}
if (node.left != null) {
calculate(node.left);
}
count++;
if (count == k) {
this.val = node.val;
return;
}
if (node.right != null) {
calculate(node.right);
}
}
}
Time Complexity (Big O Time):
The time complexity of this program depends on the structure of the BST and the value of “k.”
-
In the worst case, if the BST is completely unbalanced (skewed), the program may have to traverse all nodes in the BST, resulting in a time complexity of O(n), where “n” is the number of nodes in the tree. This occurs when k is equal to the total number of nodes in the BST.
-
In the best case, if the BST is balanced, and “k” is small (much less than n), the program can find the kth smallest element more efficiently. In a balanced BST, the height of the tree is approximately log₂(n), and the program may terminate early when it finds the kth smallest element, resulting in a time complexity closer to O(log n).
Therefore, the time complexity is typically between O(log n) and O(n), depending on the structure of the BST and the value of “k.”
Space Complexity (Big O Space):
The space complexity of this program is determined by the recursion stack and a few integer variables.
-
Recursion Stack: The program uses recursion to traverse the BST. The maximum depth of the recursion stack is equal to the height of the BST. In the worst case (completely unbalanced BST), the height could be “n,” resulting in O(n) space complexity for the recursion stack. In the best case (balanced BST), the height is approximately log₂(n), resulting in O(log n) space complexity.
-
Integer Variables: The program uses a few integer variables (k, count, val), which occupy constant space. Therefore, the space complexity due to integer variables is O(1).
In summary, the overall space complexity is O(n) in the worst case due to the recursion stack and O(log n) to O(1) in the best case, depending on the height of the BST. The time complexity ranges from O(log n) to O(n) depending on the structure of the BST and the value of “k.”

