LeetCode-in-Java
199. Binary Tree Right Side View
Medium
Given the root of a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the right side of it, return the values of the nodes you can see ordered from top to bottom.
Example 1:
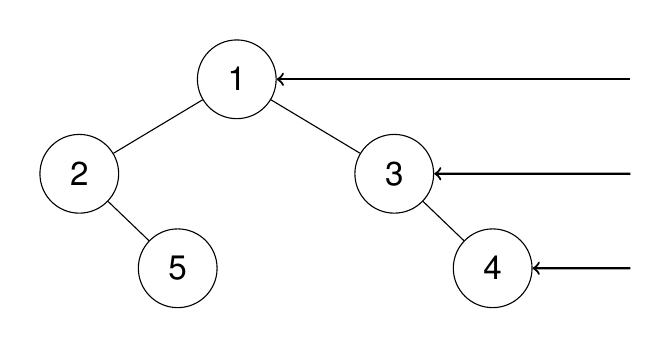
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
Output: [1,3,4]
Explanation:
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,null,null,null,5]
Output: [1,3,4,5]
Explanation:

Example 3:
Input: root = [1,null,3]
Output: [1,3]
Example 4:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Solution
import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/*
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
recurse(root, 0, list);
return list;
}
private void recurse(TreeNode node, int level, List<Integer> list) {
if (node != null) {
if (list.size() < level + 1) {
list.add(node.val);
}
recurse(node.right, level + 1, list);
recurse(node.left, level + 1, list);
}
}
}

