LeetCode-in-Java
114. Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List
Medium
Given the root of a binary tree, flatten the tree into a “linked list”:
- The “linked list” should use the same
TreeNodeclass where therightchild pointer points to the next node in the list and theleftchild pointer is alwaysnull. - The “linked list” should be in the same order as a pre-order traversal of the binary tree.
Example 1:
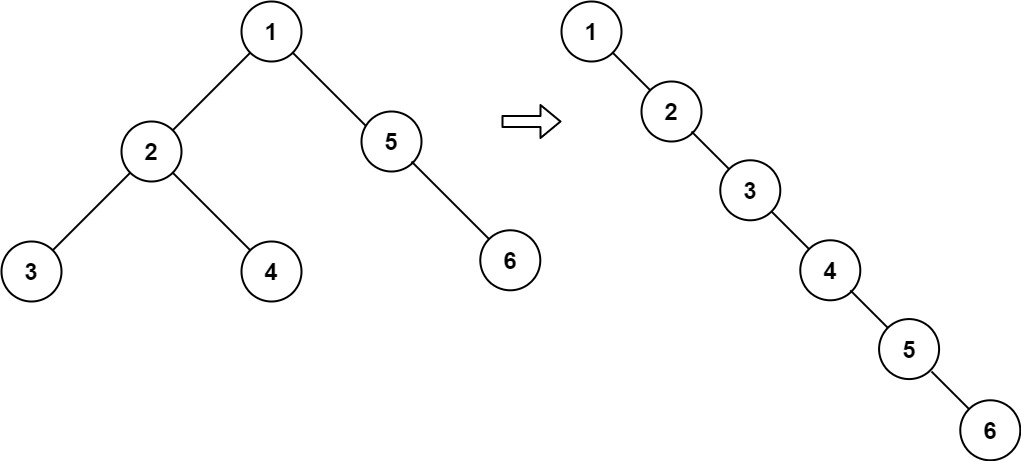
Input: root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6]
Output: [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
Example 2:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [0]
Output: [0]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 2000]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Can you flatten the tree in-place (with O(1) extra space)?
To solve the “Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List” problem in Java with a Solution class, we’ll use a recursive approach. Below are the steps:
-
Create a
Solutionclass: Define a class namedSolutionto encapsulate our solution methods. -
Create a
flattenmethod: This method takes the root node of the binary tree as input and flattens the tree into a linked list using preorder traversal. -
Check for null root: Check if the root is null. If so, there’s no tree to flatten, so return.
- Recursively flatten the tree: Define a recursive helper method
flattenTreeto perform the flattening.- The method should take the current node as input.
- Perform a preorder traversal of the tree.
- For each node, if it has a left child:
- Find the rightmost node in the left subtree.
- Attach the right subtree of the current node to the right of the rightmost node.
- Move the left subtree to the right subtree position.
- Set the left child of the current node to null.
- Recursively call the method for the right child.
- Call the helper method: Call the
flattenTreemethod with the root node.
Here’s the Java implementation:
class Solution {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return; // Check for empty tree
flattenTree(root); // Flatten the tree
}
// Recursive helper method to flatten the tree
private void flattenTree(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return;
// Flatten left subtree
flattenTree(node.left);
// Flatten right subtree
flattenTree(node.right);
// Save right subtree
TreeNode rightSubtree = node.right;
// Attach left subtree to the right of the current node
node.right = node.left;
// Set left child to null
node.left = null;
// Move to the rightmost node of the flattened left subtree
TreeNode current = node;
while (current.right != null) {
current = current.right;
}
// Attach the saved right subtree to the right of the rightmost node
current.right = rightSubtree;
}
// TreeNode definition
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
This implementation follows the steps outlined above and efficiently flattens the binary tree into a linked list using preorder traversal in Java.

