LeetCode-in-Java
109. Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree
Medium
Given the head of a singly linked list where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height balanced BST.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differ by more than 1.
Example 1:
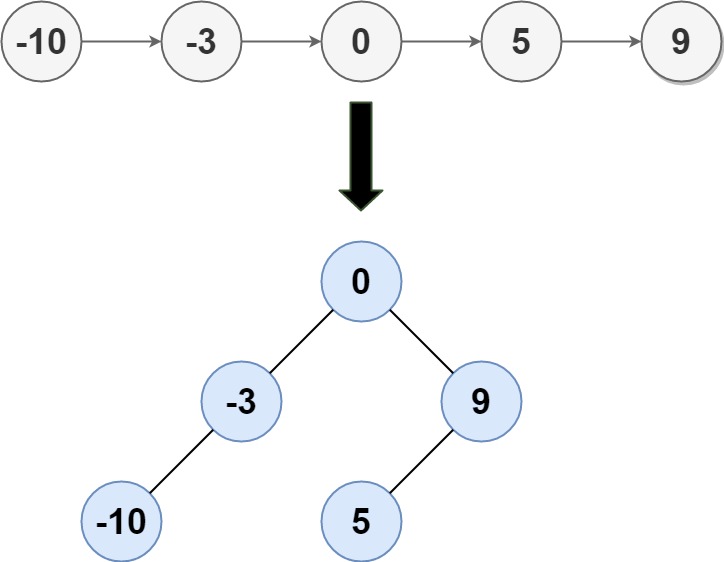
Input: head = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5]
Explanation: One possible answer is [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the shown height balanced BST.
Example 2:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [0]
Output: [0]
Example 4:
Input: head = [1,3]
Output: [3,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in
headis in the range[0, 2 * 104]. -105 <= Node.val <= 105
Solution
import com_github_leetcode.ListNode;
import com_github_leetcode.TreeNode;
/*
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
/*
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
// Empty list -> empty tree / sub-tree
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
// No next node -> this node will become leaf
if (head.next == null) {
TreeNode leaf = new TreeNode(head.val);
leaf.left = null;
leaf.right = null;
return leaf;
}
ListNode slow = head;
// Head-Start fast by 1 to get slow = mid -1
ListNode fast = head.next.next;
// Find the mid of list
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// slow.next -> mid = our "root"
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(slow.next.val);
// Right sub tree from mid - end
root.right = sortedListToBST(slow.next.next);
// Left sub tree from head - mid (chop slow.next)
slow.next = null;
root.left = sortedListToBST(head);
return root;
}
}

