LeetCode-in-Java
19. Remove Nth Node From End of List
Medium
Given the head of a linked list, remove the nth node from the end of the list and return its head.
Example 1:
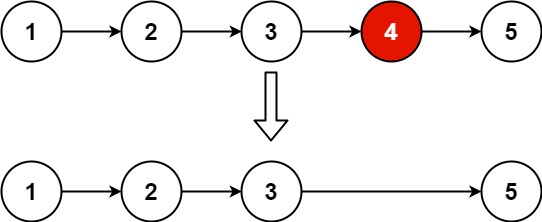
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
Output: [1,2,3,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [1], n = 1
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [1,2], n = 1
Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is
sz. 1 <= sz <= 300 <= Node.val <= 1001 <= n <= sz
Follow up: Could you do this in one pass?
To solve the Remove Nth Node From End of List problem in Java with a Solution class, we’ll follow these steps:
- Define a
ListNodeclass representing the nodes of the linked list. - Define a
Solutionclass with a method namedremoveNthFromEndthat takes the head of the linked list and an integernas input and returns the head of the modified list. - Create two pointers,
fastandslow, and initialize them to point to the head of the list. - Move the
fastpointernsteps forward in the list. - If the
fastpointer reaches the end of the list (fast == null), it means thatnis equal to the length of the list. In this case, remove the head node by returninghead.next. - Move both
fastandslowpointers simultaneously until thefastpointer reaches the end of the list. - At this point, the
slowpointer will be pointing to the node just before the node to be removed. - Remove the
nthnode by updating thenextreference of the node pointed to by theslowpointer to skip thenthnode. - Return the head of the modified list.
Here’s the implementation:
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
}
public class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode fast = dummy;
ListNode slow = dummy;
// Move the fast pointer n steps forward
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
fast = fast.next;
}
// Move both pointers until the fast pointer reaches the end
while (fast != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
// Remove the nth node
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
// Example 1
ListNode head1 = new ListNode(1);
head1.next = new ListNode(2);
head1.next.next = new ListNode(3);
head1.next.next.next = new ListNode(4);
head1.next.next.next.next = new ListNode(5);
int n1 = 2;
ListNode result1 = solution.removeNthFromEnd(head1, n1);
printList(result1); // Output: [1,2,3,5]
// Example 2
ListNode head2 = new ListNode(1);
int n2 = 1;
ListNode result2 = solution.removeNthFromEnd(head2, n2);
printList(result2); // Output: []
// Example 3
ListNode head3 = new ListNode(1);
head3.next = new ListNode(2);
int n3 = 1;
ListNode result3 = solution.removeNthFromEnd(head3, n3);
printList(result3); // Output: [1]
}
private static void printList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("[]");
return;
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("[");
while (head != null) {
sb.append(head.val).append(",");
head = head.next;
}
sb.setLength(sb.length() - 1);
sb.append("]");
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
}
This implementation provides a solution to the Remove Nth Node From End of List problem in Java.

