LeetCode-in-Java
2. Add Two Numbers
Medium
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order, and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example 1:
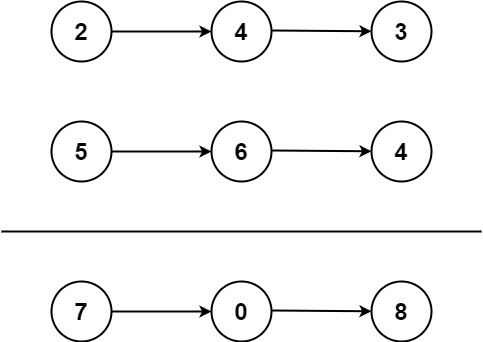
Input: l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
Output: [7,0,8]
Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.
Example 2:
Input: l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
Output: [0]
Example 3:
Input: l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9]
Output: [8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each linked list is in the range
[1, 100]. 0 <= Node.val <= 9- It is guaranteed that the list represents a number that does not have leading zeros.
To solve the Add Two Numbers problem in Java using a Solution class, we’ll follow these steps:
- Define a
ListNodeclass to represent nodes in a linked list. - Define a
Solutionclass with a method namedaddTwoNumbers. - Inside the
addTwoNumbersmethod, traverse both input linked lists simultaneously:- Keep track of a carry variable to handle cases where the sum of two digits exceeds 9.
- Calculate the sum of the current nodes’ values along with the carry.
- Update the carry for the next iteration.
- Create a new node with the sum % 10 and attach it to the result linked list.
- Move to the next nodes in both input lists.
- After finishing the traversal, check if there is any remaining carry. If so, add a new node with the carry to the result.
- Return the head of the result linked list.
Here’s the implementation:
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {}
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
public class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode();
ListNode curr = dummyHead;
int carry = 0;
while (l1 != null || l2 != null) {
int sum = carry;
if (l1 != null) {
sum += l1.val;
l1 = l1.next;
}
if (l2 != null) {
sum += l2.val;
l2 = l2.next;
}
curr.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
curr = curr.next;
carry = sum / 10;
}
if (carry > 0) {
curr.next = new ListNode(carry);
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
// Helper method to print a linked list
public void printList(ListNode head) {
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
System.out.print(curr.val + " ");
curr = curr.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
// Test cases
ListNode l1 = new ListNode(2, new ListNode(4, new ListNode(3)));
ListNode l2 = new ListNode(5, new ListNode(6, new ListNode(4)));
ListNode result1 = solution.addTwoNumbers(l1, l2);
System.out.print("Example 1 Output: ");
solution.printList(result1);
ListNode l3 = new ListNode(0);
ListNode l4 = new ListNode(0);
ListNode result2 = solution.addTwoNumbers(l3, l4);
System.out.print("Example 2 Output: ");
solution.printList(result2);
ListNode l5 = new ListNode(9, new ListNode(9, new ListNode(9, new ListNode(9, new ListNode(9, new ListNode(9, new ListNode(9)))))));
ListNode l6 = new ListNode(9, new ListNode(9, new ListNode(9, new ListNode(9))));
ListNode result3 = solution.addTwoNumbers(l5, l6);
System.out.print("Example 3 Output: ");
solution.printList(result3);
}
}
This implementation provides a solution to the Add Two Numbers problem using linked lists in Java.

